Mapping the global research landscape on malnutrition for patients with chronic kidney disease: a visualization analysis
- PMID: 37742012
- PMCID: PMC10517565
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-023-00445-8
Mapping the global research landscape on malnutrition for patients with chronic kidney disease: a visualization analysis
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is seen as a diverse disease and a primary contributor to global mortality. Malnutrition arises within chronic illness, which involves protein energy depletion and inadequate levels of essential nutrients. These factors increase the likelihood of death and the overall impact of the disease on affected individuals. Consequently, this study aims to utilize bibliometric and visual analysis to assess the current state of research, the latest advances and emerging patterns in the fields of CKD and malnutrition.
Methods: Extensive research was conducted using the Scopus database, which is the most authoritative database of research publications and citations, to focus on CKD research between 2003 and 2022, as indicated by title and author keywords. Then, within this vast collection of academic publications, a notable subset of articles was exclusively dedicated to investigating the relationship between CKD and malnutrition. Finally, we performed bibliometric analysis and visualization using VOSviewer 1.6.19 and Microsoft Excel 2013.
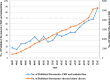
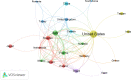
Results: Large global research between 2003 and 2022 resulted in 50,588 documents focused on CKD, as indicated by title and author keywords. In this extensive collection of scientific publications, a staggering portion of 823 articles is devoted exclusively to investigating the link between CKD and malnutrition. Further analysis reveals that this body of work consists of 565 articles (68.65%), 221 reviews (26.85%), and 37 miscellaneous entries (4.50%), which encompass letters and editorials. The USA was found to be the most productive country (n = 173; 21.02%), followed by Italy (n = 83; 10.09%), Sweden (n = 56; 6.80%), Brazil (n = 54; 6.56%) and China (n = 51; 6.20%). The most common terms on the map include those related to the topic of (a) malnutrition in hemodialysis patients and predicting factors; terms associated with the (b) impact of malnutrition on cardiovascular risk and complications in CKD patients; and terms related to the (c) dietary protein intake and malnutrition in CKD.
Conclusions: This study is the first of its kind to analyze CKD and malnutrition research using data from Scopus for visualization and network mapping. Recent trends indicate an increasing focus on protein-energy wasting/malnutrition in hemodialysis patients and predicting factors, dietary protein intake, and malnutrition in CKD. These topics have gained significant attention and reflect the latest scientific advances. Intervention studies are crucial to examining diet therapy's impact on patients with stages 1 to 5 CKD. We hope this study will offer researchers, dietitians and nephrologists valuable information.
Keywords: Bibliometric; Chronic kidney disease; Malnutrition; Scopus; VOSviewer.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bibliometric mapping of the landscape and structure of nutrition and depression research: visualization analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Apr 15;42(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00378-2. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37061731 Free PMC article.
-
Current status and development trends in CKD with frailty research from 2000 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2292142. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2292142. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38178378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Mapping the global research landscape on depression for patients with chronic kidney disease: a bibliometric and visualized analysis from 2006 to 2022.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1388641. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1388641. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39086390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the global research landscape on nutritional support for patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: visualization analysis.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Feb 22;31(3):179. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07645-2. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36810807 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel statistically equivalent signature-based hybrid feature selection and ensemble deep learning LSTM and GRU for chronic kidney disease classification.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Nov 13;10:e2467. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2467. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39678272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nugent RA, Fathima SF, Feigl AB, Chyung D. The burden of chronic kidney disease on developing nations: a 21st century challenge in global health. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;118(3):c269–277. - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2021;398(10302):786–802. - PubMed
-
- Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017;389(10075):1238–1252. - PubMed
-
- Romagnani P, Remuzzi G, Glassock R, Levin A, Jager KJ, Tonelli M, Massy Z, Wanner C, Anders HJ. Chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:17088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

