Metacognition in Community-Dwelling Older Black and African American Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37742635
- PMCID: PMC10757653
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-221140
Metacognition in Community-Dwelling Older Black and African American Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background: Cognitive assessment of older adults typically includes symptom reports and objective evaluations. However, there is often poor agreement between these measures. Cultural norms, stress, and anxiety may also influence cognitive self-appraisal and performance. Little research describes how other factors affect the self-report/objective test discrepancies noted in the literature.
Objective: This study investigated whether the disparity between subjective cognitive concerns and objective cognitive performance is related to measures of anxiety and stress in older Black and African American adults.
Methods: Telephone screenings were administered to 206 older adults (ages 64-94) during the first year of the pandemic. Demographic data, objective memory (Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status [TICS-m]), an adaptation of the subjective memory measure, the Cognitive Change Questionnaire, emphasizing executive functioning in everyday life [CCQ-e]), Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7), and Perceived Stress Scale-4 (PSS4) were measured. Metacognition Discrepancy Index (MDI) was calculated from the standardized residual after regressing TICS-m on CCQ-e scores to quantify the discrepancy between cognitive self-appraisal and objective cognitive functioning.
Results: Neither GAD-7 nor PSS-4 moderated the relationship between TICS-m and CCQ-e, and TICS-m scores weakly predicted subjective CCQ-e scores (F(1, 197)=4.37, p = 0.038, R2 = 0.022). The MDI correlated with stress and anxiety (rs = 0.294, 0.396, ps < 0.001).
Conclusion: Discrepancies exist between objectively measured and self-evaluated cognition. Elevations in stress and anxiety are associated with greater overestimation of cognitive difficulties relative to objective performance. Pandemic-related stressors may have worsened anxiety and diminished self-appraisal of cognitive abilities for some individuals, while others may remain reluctant to acknowledge impairments. Social and emotional factors are meaningful considerations in assessing cognitive difficulties.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; affect; anxiety; cognitive decline; metacognition; psychological stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest/Disclosure Statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
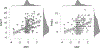

References
-
- Jessen F, Wiese B, Bachmann C, Eifflaender-Gorfer S, Haller F, Kölsch H, … & Bickel H (2010) Prediction of dementia by subjective memory impairment: effects of severity and temporal association with cognitive impairment. Archives of general psychiatry, 67(4), 414–422. - PubMed
-
- Pike KE, Cavuoto MG, Li L, Wright BJ, & Kinsella GJ (2021) Subjective cognitive decline: level of risk for future dementia and mild cognitive impairment, a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Neuropsychology Review, 1–33. - PubMed
-
- Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, … & Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging‐Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & dementia, 7(3), 270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burmester B, Leathem J, & Merrick P (2016) Subjective cognitive complaints and objective cognitive function in aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis of recent cross-sectional findings. Neuropsychology Review, 26(4), 376–393. - PubMed
-
- Crumley JJ, Stetler CA, & Horhota M (2014) Examining the relationship between subjective and objective memory performance in older adults: a meta-analysis. Psychology and Aging, 29(2), 250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

