Discovery of cancer-preventive juices reactivating RB functions
- PMID: 37743524
- PMCID: PMC10519803
- DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.23-00160
Discovery of cancer-preventive juices reactivating RB functions
Abstract
Background: Recent advances have been achieved in the genetic diagnosis and therapies against malignancies due to a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying carcinogenesis. Since active preventive methods are currently insufficient, the further development of appropriate preventive strategies is desired.
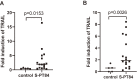
Methods: We searched for drinks that reactivate the functions of tumor-suppressor retinoblastoma gene (RB) products and exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. We also examined whether lactic acid bacteria increased the production of the cancer-specific anti-tumor cytokine, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), in human, and examined whether the RB-reactivating drinks with lactic acid bacteria decreased azoxymethane-induced rat colon aberrant crypt foci (ACF) and aberrant crypts (ACs) in vivo.
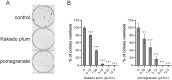
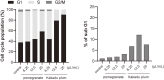
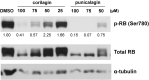
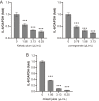
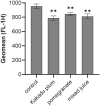
Results: Kakadu plum juice and pomegranate juice reactivated RB functions, which inhibited the growth of human colon cancer LIM1215 cells by G1 phase arrest. These juices also exerted anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Lactiplantibacillus (L.) pentosus S-PT84 was administered to human volunteers and increased the production of TRAIL. In an in vivo study, Kakadu plum juice with or without pomegranate juice and S-PT84 significantly decreased azoxymethane-induced rat colon ACF and ACs.
Conclusions: RB is one of the most important molecules suppressing carcinogenesis, and to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate that natural drinks reactivated the functions of RB. As expected, Kakadu plum juice and pomegranate juice suppressed the growth of LIM1215 cells by reactivating the functions of RB, and Kakadu plum juice with or without pomegranate juice and S-PT84 inhibited rat colon ACF and ACs. Therefore, this mixed juice has potential as a novel candidate for cancer prevention.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory effects; Antioxidant effects; Cancer prevention; Juice; Kakadu plum; Lactic acid bacteria; Pomegranate; Retinoblastoma gene; Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pomegranate polyphenolics suppressed azoxymethane-induced colorectal aberrant crypt foci and inflammation: possible role of miR-126/VCAM-1 and miR-126/PI3K/AKT/mTOR.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Dec;34(12):2814-22. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt295. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23996930
-
Beta-escin inhibits colonic aberrant crypt foci formation in rats and regulates the cell cycle growth by inducing p21(waf1/cip1) in colon cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Jun;5(6):1459-66. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0495. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16818504
-
Chemoprevention of colon cancer carcinogenesis by balsalazide: inhibition of azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypt formation in the rat colon and intestinal tumor formation in the B6-Min/+ mouse.Int J Oncol. 2000 Jul;17(1):173-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.17.1.173. Int J Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10853036
-
Diosgenin, a steroid saponin of Trigonella foenum graecum (Fenugreek), inhibits azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypt foci formation in F344 rats and induces apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004 Aug;13(8):1392-8. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004. PMID: 15298963
-
Azoxymethane-induced rat aberrant crypt foci: relevance in studying chemoprevention of colon cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Nov 21;14(43):6632-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6632. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19034964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer prevention: past challenges and future directions.Genes Environ. 2025 Feb 27;47(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s41021-025-00326-y. Genes Environ. 2025. PMID: 40011962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the Effects of Tannase on the De Astringency of Pomegranate Juice.Foods. 2025 Mar 14;14(6):985. doi: 10.3390/foods14060985. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40231994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishikawa H, Mutoh M, Sato Y, Doyama H, Tajika M, Tanaka S, et al.. Chemoprevention with low-dose aspirin, mesalazine, or both in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis without previous colectomy (J-FAPP Study IV): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, two-by-two factorial design trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:474–81. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00018-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aune D, Giovannucci E, Boffetta P, Fadnes LT, Keum N, Norat T, et al.. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46:1029–56. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

