Effectiveness of BNT162b2 Against Infection, Symptomatic Infection, and Hospitalization Among Older Adults Aged ≥65 Years During the Delta Variant Predominance in Japan: The VENUS Study
- PMID: 37743530
- PMCID: PMC11078592
- DOI: 10.2188/jea.JE20230106
Effectiveness of BNT162b2 Against Infection, Symptomatic Infection, and Hospitalization Among Older Adults Aged ≥65 Years During the Delta Variant Predominance in Japan: The VENUS Study
Abstract
Background: We evaluated the effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine against infection, symptomatic infection, and hospitalization in older people during the Delta-predominant period (July 1 to September 30, 2021).
Methods: We performed a population-based cohort study in an older adult population aged ≥65 years using data from the Vaccine Effectiveness, Networking, and Universal Safety Study conducted from January 1, 2019, to September 30, 2021, in Japan. We matched BNT162b2-vaccinated and -unvaccinated individuals in a 1:1 ratio on the date of vaccination of the vaccinated individual. We evaluated the effectiveness of the vaccine against infection, symptomatic infection, and coronavirus disease (COVID-19)-related hospitalization by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. We estimated the risk ratio and risk difference using the Kaplan-Meier method with inverse probability weighting. The vaccine effectiveness was calculated as (1 - risk ratio) × 100%.
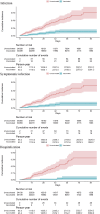
Results: The study included 203,574 matched pairs aged ≥65 years. At 7 days after the second dose, the vaccine effectiveness of BNT162b2 against infection, symptomatic infection, and hospitalization was 78.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 65.2-87.8%), 79.1% (95% CI, 64.6-88.9%), and 93.5% (95% CI, 83.7-100%), respectively.
Conclusion: BNT162b2 was highly effective against infection, symptomatic infection, and hospitalization in Japan's older adult population aged ≥65 years during the Delta-predominant period.
Keywords: Delta variant; Japan; SARS-CoV-2 infection; cohort study; mRNA vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Listings of WHO’s response to COVID-19. Accessed September 15, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline.
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Visualizing the data: information on COVID-19 infections. Accessed October 19, 2022. https://covid19.mhlw.go.jp/en/.
-
- Current Situation of Infection, May 12, 2021. Published May 20, 2021. Accessed September 22, 2022. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/2019-ncov-e/10381-covid19-ab34th-en.html.
-
- Current Situation of Infection, June 23, 2021. Published July 1, 2021. Accessed September 22, 2022. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/2019-ncov-e/10492-covid19-ab40th-en.html.
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Current Situation of Infection, September 1, 2021. Published September 10, 2021. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/2019-ncov-e/10636-covid19-ab50th-en.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous