Factors associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes of maternal syphilis in Henan, China, 2016-2022
- PMID: 37743831
- PMCID: PMC10600900
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268823001589
Factors associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes of maternal syphilis in Henan, China, 2016-2022
Abstract
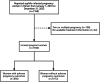
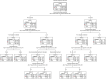
Maternal syphilis not only seriously affects the quality of life of pregnant women themselves but also may cause various adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs). This study aimed to analyse the association between the related factors and APOs in maternal syphilis. 7,030 pregnant women infected with syphilis in Henan Province between January 2016 and December 2022 were selected as participants. Information on their demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment status, and pregnancy outcomes was collected. Multivariate logistic regression models and chi-squared automatic interaction detector (CHAID) decision tree models were used to analyse the factors associated with APOs. The multivariate logistic regression results showed that the syphilis infection history (OR = 1.207, 95% CI, 1.035-1.409), the occurrence of abnormality during pregnancy (OR = 5.001, 95% CI, 4.203-5.951), not receiving standard treatment (OR = 1.370, 95% CI, 1.095-1.716), not receiving any treatment (OR = 1.313, 95% CI, 1.105-1.559), and a titre ≥1:8 at diagnosis (OR = 1.350, 95%CI, 1.079-1.690) and before delivery (OR = 1.985, 95%CI, 1.463-2.694) were risk factors. A total of six influencing factors of APOs in syphilis-infected women were screened using the CHAID decision tree model. Integrated prevention measures such as early screening, scientific eugenics assessment, and standard syphilis treatment are of great significance in reducing the incidence of APOs for pregnant women infected with syphilis.
Keywords: adverse pregnancy outcomes; associated factors; decision tree model; pregnancy; syphilis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and associated predictors of adverse pregnancy outcomes of maternal syphilis in China, 2016-19: a Cox regression analysis.BJOG. 2021 May;128(6):994-1002. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16554. Epub 2020 Dec 22. BJOG. 2021. PMID: 33021043
-
The Effect of Different Treatment Regimens and Multiple Risk Factors on Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes among Syphilis-Seropositive Women in Guangzhou: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 1;2020:7626274. doi: 10.1155/2020/7626274. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32462016 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with preterm birth and mother-to-child transmission in HIV-positive pregnant women in Henan, China, 2016-2022: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2024 Dec 15;14(12):e082805. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082805. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39675820 Free PMC article.
-
Towards the elimination of mother to child transmission of syphilis 2015-2020: practice and progress in Zhejiang province, eastern China.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Feb 7;23(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05258-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 36750770 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and perinatal risk factors associated with congenital syphilis.Trop Med Int Health. 2023 Jun;28(6):442-453. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13881. Epub 2023 May 8. Trop Med Int Health. 2023. PMID: 37156513 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis and forecasting of syphilis trends in mainland China based on hybrid time series models.Epidemiol Infect. 2024 May 27;152:e93. doi: 10.1017/S0950268824000694. Epidemiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38800855 Free PMC article.
-
Factors related to adverse pregnancy outcomes of maternal syphilis in Nanning, Guangxi, China 2016-2020.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 5;15(1):28591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11884-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40764630 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Cohort Study on Treponema pallidum Infection: Clinical Trends and Treatment Outcomes for Congenital Syphilis in Guangxi, China (2013-2023).Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 12;17:2351-2359. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S467426. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38882653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee K, You S, Li Y, Chesson H, Gift TL, Berruti AA, Hsu K, Yaesoubi R, Salomon JA and Rönn M. (2023) Estimation of the lifetime quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) lost due to syphilis acquired in the United States in 2018. Clinical Infectious Disease 76, e810–e819. 10.1093/cid/ciac427 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical