Antagonism among DUX family members evolved from an ancestral toxic single homeodomain protein
- PMID: 37744032
- PMCID: PMC10514451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107823
Antagonism among DUX family members evolved from an ancestral toxic single homeodomain protein
Abstract
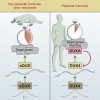
Double homeobox (DUX) genes are unique to eutherian mammals, expressed transiently during zygotic genome activation (ZGA) and involved in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) and cancer when misexpressed. We evaluate the 3 human DUX genes and the ancestral single homeobox gene sDUX from the non-eutherian mammal, platypus, and find that DUX4 cytotoxicity is not shared with DUXA or DUXB, but surprisingly is shared with platypus sDUX, which binds DNA as a homodimer and activates numerous ZGA genes and long terminal repeat (LTR) elements. DUXA, although transcriptionally inactive, has DNA binding overlap with DUX4, and DUXA-VP64 activates DUX4 targets and is cytotoxic. DUXA competition antagonizes the activity of DUX4 on its target genes, including in FSHD patient cells. Since DUXA is a DUX4 target gene, this competition potentiates feedback inhibition, constraining the window of DUX4 activity. The DUX gene family therefore comprises antagonistic members of opposing function, with implications for their roles in ZGA, FSHD, and cancer.
Keywords: Developmental genetics; Evolutionary developmental biology; Molecular interaction; Molecular toxicology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Update of
-
Antagonism among DUX family members evolved from an ancestral toxic single homeodomain protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 22:2023.01.21.524976. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.21.524976. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: iScience. 2023 Sep 02;26(10):107823. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107823. PMID: 36711898 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Gabriëls J., Beckers M.C., Ding H., De Vriese A., Plaisance S., van der Maarel S.M., Padberg G.W., Frants R.R., Hewitt J.E., Collen D., et al. Nucleotide sequence of the partially deleted D4Z4 locus in a patient with FSHD identifies a putative gene within each 3.3 kb element. Gene. 1999;236:25–32. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00267-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Overveld P.G.M., Lemmers R.J.F.L., Sandkuijl L.A., Enthoven L., Winokur S.T., Bakels F., Padberg G.W., van Ommen G.J.B., Frants R.R., et al. Hypomethylation of D4Z4 in 4q-linked and non-4q-linked facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 2003;35:315–317. - PubMed
-
- Snider L., Geng L.N., Lemmers R.J.L.F., Kyba M., Ware C.B., Nelson A.M., Tawil R., Filippova G.N., van der Maarel S.M., Tapscott S.J., et al. Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy: incomplete suppression of a retrotransposed gene. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001181. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

