The evolution of extra-pair paternity and paternal care in birds
- PMID: 37744165
- PMCID: PMC10516673
- DOI: 10.1093/beheco/arad053
The evolution of extra-pair paternity and paternal care in birds
Abstract
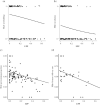
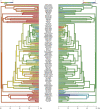
Extra-pair paternity (EPP) influences the relatedness between social parents and offspring. Therefore, one might expect the level of EPP to influence levels of paternal investment. Here, we investigated the effect of variation in EPP rates on male contributions to parental care within a phylogenetic framework of up to 271 primarily socially monogamous bird species representing 85 families. We used proportion of male provisioning and occurrence of male incubation and nestbuilding as measures of paternal care. We tested the relationship between EPP rates and different components of paternal care while controlling for various life-history traits, namely lifespan, clutch size, and body mass in a phylogenetic path analysis framework. EPP was significantly negatively associated with the occurrence (i.e., whether males participate or not) of male nestbuilding and incubation, but not with the relative amount (proportion) of nestbuilding or incubation performed by the male. Importantly, the proportion of provisioning and biomass delivery by males was clearly negatively associated with EPP. These analyses thus confirm that the effect of EPP on proportion of provisioning visits by males is similar to proportion of biomass delivery, an often assumed but rarely tested assumption. Analysing only Passerine species provided similar results, although only proportion of provisioning was significantly negatively associated with EPP. This study, therefore, provides the most comprehensive support to date of a negative relationship between EPP and paternal care across species. However, a causal relationship between EPP and paternal care cannot necessarily be concluded. We also identify key methodological improvements for future research within the topic.
Keywords: extra-pair paternity; incubation; life history; nestbuilding; parental care; phylogenetic path analysis; provisioning.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Society for Behavioral Ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett PM, Owens IP.. 2002. Evolutionary ecology of birds-life histories, mating systems and extinction. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
-
- Clutton-Brock TH. 1991. The evolution of parental care. In: The evolution of parental care. Princeton University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

