Peptide-conjugated antimiRs improve myotonic dystrophy type 1 phenotypes by promoting endogenous MBNL1 expression
- PMID: 37744174
- PMCID: PMC10514136
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.09.001
Peptide-conjugated antimiRs improve myotonic dystrophy type 1 phenotypes by promoting endogenous MBNL1 expression
Abstract
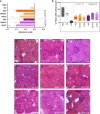
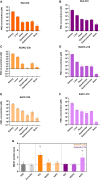
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is a rare neuromuscular disease caused by a CTG repeat expansion in the DMPK gene that generates toxic RNA with a myriad of downstream alterations in RNA metabolism. A key consequence is the sequestration of alternative splicing regulatory proteins MBNL1/2 by expanded transcripts in the affected tissues. MBNL1/2 depletion interferes with a developmental alternative splicing switch that causes the expression of fetal isoforms in adults. Boosting the endogenous expression of MBNL proteins by inhibiting the natural translational repressors miR-23b and miR-218 has previously been shown to be a promising therapeutic approach. We designed antimiRs against both miRNAs with a phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotide (PMO) chemistry conjugated to cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) to improve delivery to affected tissues. In DM1 cells, CPP-PMOs significantly increased MBNL1 levels. In some candidates, this was achieved using concentrations less than two orders of magnitude below the median toxic concentration, with up to 5.38-fold better therapeutic window than previous antagomiRs. In HSALR mice, intravenous injections of CPP-PMOs improve molecular, histopathological, and functional phenotypes, without signs of toxicity. Our findings place CPP-PMOs as promising antimiR candidates to overcome the treatment delivery challenge in DM1 therapy.
Keywords: MBNL proteins; MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; PMO chemistry; alternative splicing; antisense oligonucleotides; biodistribution; cell-penetrating peptides; microRNAs; muscle dysfunction; myotonic dystrophy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
B.L. and R.A. are founders, and CEO and scientific consultant of Arthex Biotech, respectively. Arthex Biotech is developing antimiRs for use in the treatment of DM1.
Figures

References
-
- Brook J.D., McCurrach M.E., Harley H.G., Buckler A.J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V.P., Thirion J.P., Hudson T. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992;68:799–808. - PubMed
-
- Ozimski L.L., Sabater-Arcis M., Bargiela A., Artero R. The hallmarks of myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle dysfunction. Biol. Rev. Camb. Phil. Soc. 2021;96:716–730. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

