Real-World Response and Outcomes in Patients With NSCLC With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
- PMID: 37744306
- PMCID: PMC10514080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100558
Real-World Response and Outcomes in Patients With NSCLC With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
Abstract
Introduction: This study describes treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions (EGFRex20ins) in the United States.
Methods: The Flatiron Health electronic health record database was used to select three cohorts among patients diagnosed with NSCLC with EGFRex20ins (January 1, 2011-February 29, 2020): (1) first-line (1L) or patients receiving 1L therapy after documented EGFRex20ins; (2) second or later-line (≥2L) or patients receiving ≥2L therapy after documented EGFRex20ins; and (3) ≥2L postplatinum trial-aligned, or ≥2L patients previously treated with platinum chemotherapy whose baseline characteristics aligned with key eligibility criteria (initiating new treatment after documented EGFRex20ins and ≥1 previous treatment excluding mobocertinib or amivantamab) of the mobocertinib trial NCT02716116. Real-world end points were confirmed overall response rate, overall survival, and progression-free survival.
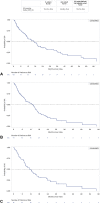
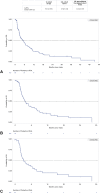
Results: Of 237 patients with EGFRex20ins-mutated NSCLC, 129 and 114 patients were included in the 1L and ≥2L cohorts, respectively. In 1L patients, platinum chemotherapy plus nonplatinum chemotherapy (31.0%) and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (28.7%) were the most common regimens. In ≥2L patients, immuno-oncology monotherapy (28.1%) and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (17.5%) were the most common index treatments. For any 1L, ≥2L, and ≥2L postplatinum trial-aligned patients, the confirmed overall response rate was 18.6%, 9.6%, and 14.0%, respectively; the median overall survival was 17.0, 13.6, and 11.5 months; the median progression-free survival was 5.2, 3.7, and 3.3 months, respectively.
Conclusions: The outcomes for patients with NSCLC with EGFRex20ins were poor. This real-world study provides a benchmark on treatment outcomes in this patient population and highlights the unmet need for improved therapeutic options.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; EGFR exon 20 insertions; Immunotherapy; Non–small cell lung cancer; Treatment outcome; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy.
© 2023 by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Rosell R., Carcereny E., Gervais R., et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Yang J.C., Shih J.Y., Su W.C., et al. Afatinib for patients with lung adenocarcinoma and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations (LUX-Lung 2): a phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:539–548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

