Updates on developing and applying biosensors for the detection of microorganisms, antimicrobial resistance genes and antibiotics: a scoping review
- PMID: 37744478
- PMCID: PMC10512422
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1240584
Updates on developing and applying biosensors for the detection of microorganisms, antimicrobial resistance genes and antibiotics: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: The inappropriate use of antibiotics in clinical and non-clinical settings contributes to the increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant microorganisms. Contemporary endeavours are focused on exploring novel technological methodologies, striving to create cost-effective and valuable alternatives for detecting microorganisms, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), and/or antibiotics across diverse matrices. Within this context, there exists an increasingly pressing demand to consolidate insights into potential biosensors and their implications for public health in the battle against antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
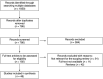
Methods: A scoping review was carried out to map the research conducted on biosensors for the detection of microorganisms, ARGs and/or antibiotics in clinical and environmental samples. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist was used. Articles published from 1999 to November 2022 and indexed in the following databases were included: MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, BIOSIS Citation index, Derwent Innovations index, and KCI-Korean Journal.
Results: The 48 studies included in the scoping review described the development and/or validation of biosensors for the detection of microorganisms, ARGs and/or antibiotics. At its current stage, the detection of microorganisms and/or ARGs has focused primarily on the development and validation of biosensors in clinical and bacterial samples. By contrast, the detection of antibiotics has focused primarily on the development and validation of biosensors in environmental samples. Asides from target and samples, the intrinsic characteristics of biosensors described in the scoping review were heterogenous. Nonetheless, the number of studies assessing the efficacy and validation of the aforementioned biosensor remained limited, and there was also a lack of comparative analyses against conventional molecular techniques.
Conclusion: Promoting high-quality research is essential to facilitate the integration of biosensors as innovative technologies within the realm of public health challenges, such as antimicrobial resistance AMR. Adopting a One-Health approach, it becomes imperative to delve deeper into these promising and feasible technologies, exploring their potential across diverse sample sets and matrices.
Keywords: antibiotic; antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobial resistance gene; biosensor; clinical samples; environment; public health.
Copyright © 2023 Magnano San Lio, Barchitta, Maugeri, La Rosa, Favara and Agodi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tackling antimicrobial resistance in primary care facilities across Pakistan: Current challenges and implications for the future.J Infect Public Health. 2023 Dec;16 Suppl 1:97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2023.10.046. Epub 2023 Nov 2. J Infect Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37973496
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Effective Treatment Strategies for the Removal of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria, Antibiotic-Resistance Genes, and Antibiotic Residues in the Effluent From Wastewater Treatment Plants Receiving Municipal, Hospital, and Domestic Wastewater: Protocol for a Systematic Review.JMIR Res Protoc. 2021 Nov 26;10(11):e33365. doi: 10.2196/33365. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34842550 Free PMC article.
-
Sensors for Smoking Detection in Epidemiological Research: Scoping Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024 Oct 30;12:e52383. doi: 10.2196/52383. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2024. PMID: 39476379 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Antibiotics in Milk: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;13(9):867. doi: 10.3390/bios13090867. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosensing technology for detection and assessment of pathogenic microorganisms.Future Microbiol. 2025 Jan;20(1):57-72. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2024.2417621. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Future Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39469851 Review.
-
Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 15;16(11):1615. doi: 10.3390/ph16111615. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Biosensor Technologies for Meat Production Chain.Foods. 2025 Feb 22;14(5):744. doi: 10.3390/foods14050744. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40077447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, Quattrocchi A, Hoxha A, Simonsen GS, et al. . Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European economic area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2019) 19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Food and Drug Administration DoHaH, Services . Summary report on antimicrobials sold or distributed for use in food-producing animals. (2022). Available at https://www.fda.gov/media/163739/download
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources