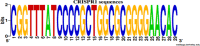CRISPR Typing of Clinical Strains of Salmonella spp. Isolated in Tehran, Iran
- PMID: 37744550
- PMCID: PMC10512146
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v52i8.13415
CRISPR Typing of Clinical Strains of Salmonella spp. Isolated in Tehran, Iran
Abstract
Background: Salmonella is one of the most leading causes of food-born infection and death among infants and people with the poor immunity system. Because Salmonella spp. have diversity in the genome composition and pathogenicity, access to rapid identification and genotyping is necessary to control of salmonellosis. The CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) typing is a genotyping method that checks these variable sequences in the bacterial genome in a specific species. This study aimed to differentiate Salmonella strains using CRISPR region.
Methods: Salmonella isolates, previously identified via standard microbiological and molecular tests, were subjected to the study. Bacterial DNA was extracted and PCR was done using specific primers. The different PCR products were sequenced and the repeats patterns were used to identify additional or degenerate repeat clusters in the CRISPR region. All different sequences were analyzed using CRISPRtionary tool for dendrogram generation using the binary file.
Results: Overall, 119 strains of various Salmonella serovars were used. The result showed unique CRISPR and diversity in spacer both in sequence and the number. Analysis of the extracted sequence and band patterns illustrated that, except for S. infantis, both S. enteritidis and S. typhimurium isolates were classified as a separate cluster.
Conclusion: CRISPR genotyping could provide serotype/spacers dictionary and it is performed at low cost and high speed in comparison to the other typing methods. Therefore, the assessment of CRISPR and spacer content can be considered as a powerful and practical discriminatory method for subtyping of Salmonella isolates.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas Systems; Genotyping; Salmonella spp..
Copyright © 2023 Karimi et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous