Plant fructans: Recent advances in metabolism, evolution aspects and applications for human health
- PMID: 37744554
- PMCID: PMC10517269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100595
Plant fructans: Recent advances in metabolism, evolution aspects and applications for human health
Abstract
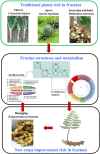
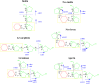
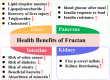
Fructans, fructose polymers, are one of the three major reserve carbohydrate in plants. The nutritional and therapeutic benefits of natural fructans in plants have attracted increasing interest by consumers and food industry. In the course of evolution, many plants have developed the ability of regulating plant fructans metabolism to produce fructans with different structures and chain lengths, which are strongly correlated with their survival in harsh environments. Exploring these evolution-related genes in fructans biosynthesis and de novo domestication of fructans-rich plants based on genome editing is a viable and promising approach to improve human dietary quality and reduce the risk of chronic disease. These advances will greatly facilitate breeding and production of tailor-made fructans as a healthy food ingredient from wild plants such as huangjing (Polygonatum cyrtonema). The purpose of this review is to broaden our knowledge on plant fructans biosynthesis, evolution and benefits to human health.
Keywords: Evolution aspects; Fructosyltransferases; Functional foods; Metabolism; Plant fructans.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between fructan metabolism and plant growth regulators.Planta. 2022 Jan 27;255(2):49. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03826-1. Planta. 2022. PMID: 35084581 Review.
-
Preparation, Structural Characterisation, and Bioactivities of Fructans: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Feb 7;28(4):1613. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041613. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of tailor-made fructans in sugar beet by expression of onion fructosyltransferase genes.Plant Biotechnol J. 2004 Jul;2(4):321-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2004.00074.x. Plant Biotechnol J. 2004. PMID: 17134393
-
Fructose-Containing Plant Carbohydrates: Biological Activities and Medical Applications.Dokl Biol Sci. 2023 Oct;512(1):343-353. doi: 10.1134/S0012496623700655. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Dokl Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38087025
-
Plant fructans in stress environments: emerging concepts and future prospects.J Exp Bot. 2008;59(11):2905-16. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern164. Epub 2008 Jul 4. J Exp Bot. 2008. PMID: 18603617 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of novel fructo-oligosaccharide bacterial consumers by pulse metatranscriptomics in a human stool sample.mSphere. 2025 Jan 28;10(1):e0066824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00668-24. Epub 2024 Dec 19. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 39699190 Free PMC article.
-
Consumption of the Prebiotic-Rich Chicory Taproot Contrasts the Cognitive and Motivational Consequences of Chronic Corticosterone Exposure and Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition in Mice.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025 Apr 28;5(4):100520. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2025.100520. eCollection 2025 Jul. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40530341 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Daylily (Hemerocallis citrina Baroni): Isolation, Structure Analysis, and Probiotics Adhesion Promotion Effect.Foods. 2024 Feb 27;13(5):721. doi: 10.3390/foods13050721. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472834 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of fructan and gluten on gut microbiota in individuals with self-reported non-celiac gluten/wheat sensitivity-a randomised controlled crossover trial.BMC Med. 2024 Sep 4;22(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03562-1. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39227818 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ahmed W., Rashid S. Functional and therapeutic potential of inulin: a comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019;59:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Anastasovska J., Arora T., Sanchez Canon G.J., Parkinson J.R.C., Touhy K., Gibson G.R., Nadkarni N.A., So P.W., Goldstone A.P., Thomas E.L., Hankir M.K., Van Loo J., Modi N., Bell J.D., Frost G. Fermentable carbohydrate alters hypothalamic neuronal activity and protects against the obesogenic environment. Obesity. 2012;20:1016–1023. - PubMed
-
- Arrizon J., Morel S., Gschaedler A., Monsan P. Comparison of the water-soluble carbohydrate composition and fructan structures of Agave tequilana plants of different ages. Food Chem. 2010;122(1):123–130.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

