Fenoxycarb, a carbamate insect growth regulator, inhibits brassinosteroid action
- PMID: 37745175
- PMCID: PMC10513946
- DOI: 10.1584/jpestics.D23-015
Fenoxycarb, a carbamate insect growth regulator, inhibits brassinosteroid action
Abstract
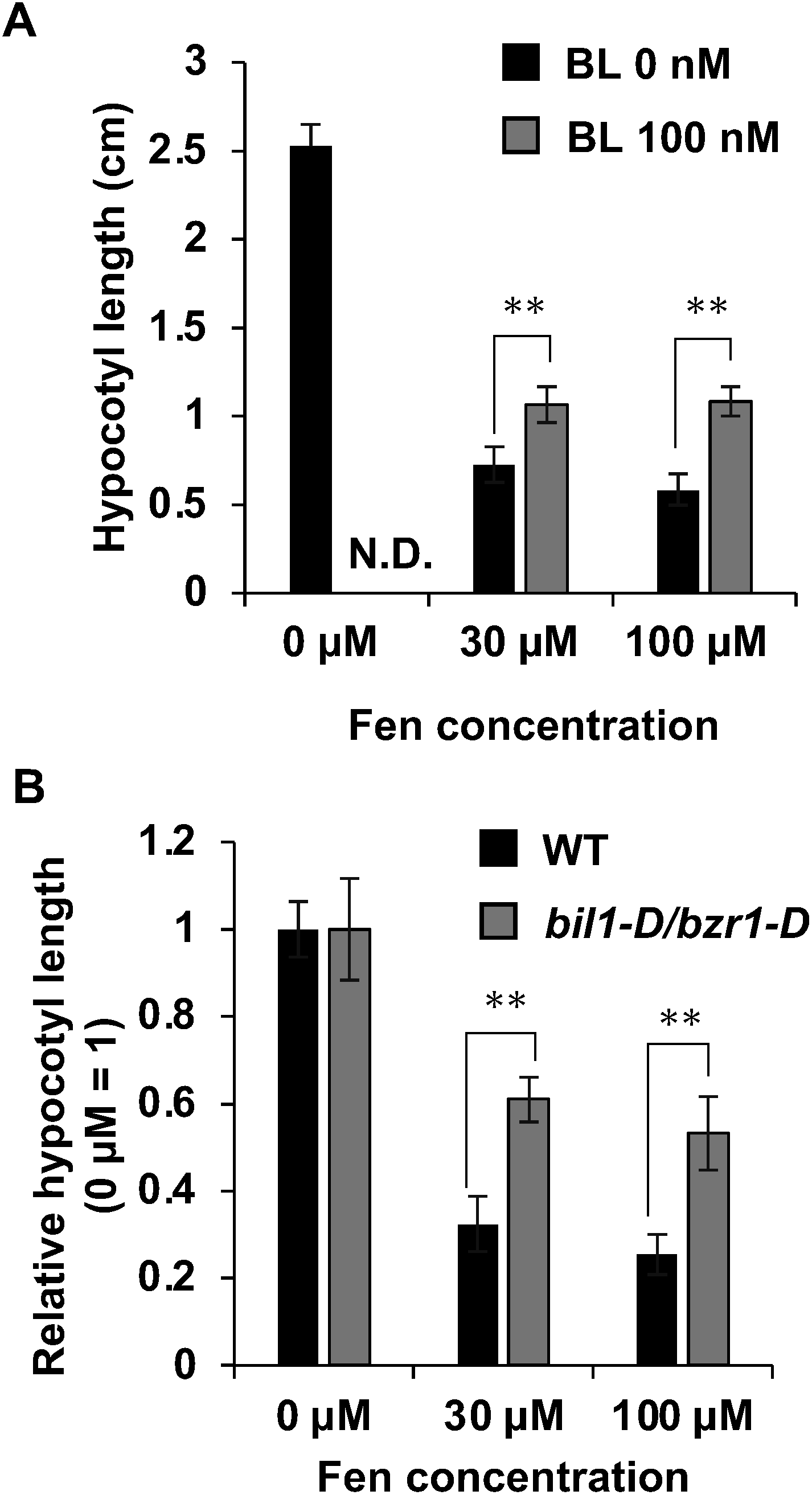
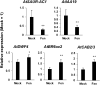
Brassinosteroids (BRs) are steroid hormones that regulate plant growth, development, and stress resistance. In this study, we evaluated the effect of agrochemicals on dark-induced hypocotyl elongation, which is regulated by BRs, to identify novel chemicals that regulate BR action. We found that the juvenile hormone agonist fenoxycarb inhibited dark-induced hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Treatment with the same class of juvenile hormone agonist, pyriproxyfen, did not affect hypocotyl elongation. Co-treatment with fenoxycarb and BR partly canceled the fenoxycarb-induced hypocotyl suppression. In addition, gene expression analysis revealed that fenoxycarb altered the BR-responsive gene expression. These results indicate that fenoxycarb is a BR action inhibitor.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; brassinosteroid; fenoxycarb; insect growth regulator.
© 2023 Pesticide Science Society of Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestDeclarations of interest: none
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of synthetic ecdysteroid analogues as functional mimics of brassinosteroids in plant growth.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;172:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 4. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28479230
-
Brassinosteroid Induces Phosphorylation of the Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase during Hypocotyl Elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2019 May 1;60(5):935-944. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz005. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30649552
-
Hypocotyl Elongation Inhibition of Melatonin Is Involved in Repressing Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Sep 26;10:1082. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01082. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31616446 Free PMC article.
-
Brassinosteroid signaling in plant development and adaptation to stress.Development. 2019 Mar 14;146(5):dev151894. doi: 10.1242/dev.151894. Development. 2019. PMID: 30872266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Brassinosteroids in Plant Reproduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 29;21(3):872. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030872. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32013254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- 2) Z. Y. Wang, T. Nakano, J. Gendron, J. He, M. Chen, D. Vafeados, Y. Yang, S. Fujioka, S. Yoshida, T. Asami and J. Chory: Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev. Cell 2, 505–513 (2002). - PubMed
-
- 3) T. Asami, T. Nakano and S. Fujioka: Plant brassinosteroid hormones. Vitam. Horm. 72, 479–504 (2005). - PubMed
-
- 4) Y. Yin, Z. Y. Wang, S. Mora-Garcia, J. Li, S. Yoshida, T. Asami and J. Chory: BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 109, 181–191 (2002). - PubMed
-
- 5) Y. Sun, X. Y. Fan, D. M. Cao, W. Tang, K. He, J. Y. Zhu, J. X. He, M. Y. Bai, S. Zhu, E. Oh, S. Patil, T. W. Kim, H. Ji, W. H. Wong, S. Y. Rhee and Z. Y. Wang: Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 19, 765–777 (2010). - PMC - PubMed

