Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Indole-Based Sulfenylated Heterobiaryls by Rhodium-Catalyzed Atroposelective Reductive Aldol Reaction
- PMID: 37745194
- PMCID: PMC10513111
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.3c03422
Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Indole-Based Sulfenylated Heterobiaryls by Rhodium-Catalyzed Atroposelective Reductive Aldol Reaction
Abstract
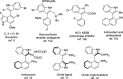
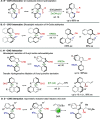
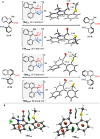
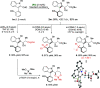
A highly enantio- and diastereoselective dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of configurationally labile 3-aryl indole-2-carbaldehydes is described. The DKR proceeds via a Rh-catalyzed intermolecular asymmetric reductive aldol reaction with acrylate esters, with simultaneous generation of three stereogenic elements. The strategy relies on the labilization of the stereogenic axis that takes place thanks to a transient Lewis acid-base interaction (LABI) between the formyl group and a thioether moiety strategically located at the ortho' position. The atropisomeric indole products present a high degree of functionalization and can be further converted to a series of axially chiral derivatives, thereby expanding their potential application in drug discovery and asymmetric catalysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Toenjes S. T.; Gustafson J. L. Atropisomerism in Medicinal Chemistry: Challenges and Opportunities. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 409–422. 10.4155/fmc-2017-0152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Clayden J.; Moran W. J.; Edwards P. J.; LaPlante S. R. The Challenge of Atropisomerism in Drug Discovery. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6398–6401. 10.1002/anie.200901719. - DOI - PubMed
- Smyth J. E.; Butler N. M.; Keller P. A. A Twist of Nature-The Significance of Atropisomers in Biological Systems. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1562–1583. 10.1039/C4NP00121D. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dotsevi G.; Sogah Y.; Cram D. J. Total Chromatographic Optical Resolution of α-Amino Acid and Ester Salts through Chiral Recognition by a Host Covalently Bound to Polystyrene Resin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 3038–3041. 10.1021/ja00426a073. - DOI - PubMed
- Takaishi K.; Yasui M.; Ema T. Binaphthyl-Bipyridyl Cyclic Dyads as a Chiroptical Switch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 5334–5338. 10.1021/jacs.8b01860. - DOI - PubMed
- Li Q.; Green L.; Venkataraman N.; Shiyanovskaya I.; Khan A.; Urbas A.; Doane J. W. Reversible Photoswitchable Axially Chiral Dopants with High Helical Twisting Power. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12908–12909. 10.1021/ja0747573. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Privileged Chiral Ligands and Catalysts; Zhou Q.-L., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011.
- Li Y.-M.; Kwong F.-Y.; Yu W.-Y.; Chan A. S.C. Recent Advances in Developing New Axially Chiral Phosphine Ligands for Asymmetric Catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2119.10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.020. - DOI
- Chen Y.; Yekta S.; Yudin A. K. Modified BINOL Ligands in Asymmetric Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3155.10.1021/cr020025b. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parmar D.; Sugiono E.; Raja S.; Rueping M. Complete Field Guide to Asymmetric BINOL-Phosphate Derived Brønsted Acid and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Brønsted Acidity, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion Pairing, and Metal Phosphates. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9047.10.1021/cr5001496. - DOI - PubMed
- Min C.; Seidel D. Asymmetric Brønsted Acid Catalysis with Chiral Carboxylic Acids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5889.10.1039/C6CS00239K. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
