First detection and molecular characterization of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) in Algeria
- PMID: 37745217
- PMCID: PMC10513046
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1235123
First detection and molecular characterization of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) in Algeria
Abstract
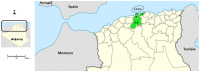
Since the first detection of rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD), the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) has been responsible for high morbidity and mortality worldwide, both in domestic and in wild rabbits. Despite the apparent control of RHD in rabbitries through vaccination, several studies highlighted the rapid evolution of RHDV by recombination, which may facilitate the emergence of new pathogenic strains. The aim of this study was to confirm the presence and characterize RHDV in Algeria. For this, rabbit samples were collected in the north of Algeria, between 2018 and 2021, from small farms where the virus was suspected after the sudden death of a high number of rabbits, and from healthy hunted wild rabbits. The domestic rabbits revealed clinical signs and lesions that were suggestive of RHD. RT-PCR showed that 79.31% of the domestic rabbit samples were positive for RHDV, while in 20.69%, including the hunted rabbits, the virus was not detected. Phylogenetic analysis of the Algerian strains allowed the confirmation and identification as GI.2 (RHDV2), and showed a close relation to GI.3P-GI.2 recombinant strains, suggesting a potential introduction from other countries, with an older strain potentially originated from neighboring Tunisia, while more recent isolates grouped with strains from North America. Our study reports for the first time the presence of GI.2 (RHDV2) in Algeria with multiple routes of introduction. Consequently, we propose that RHDV control in Algeria should be based on epidemiological surveys in association with an adequate prophylactic program.
Keywords: Algeria; GI.2; RHDV2; epidemiology; rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus; rabbits.
Copyright © 2023 Sahraoui, Lahouassa, Maziz-Bettahar, Lopes, Almeida, Ainbaziz and Abrantes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

