Morphological and molecular characterization of Haemonchus contortus isolated from the small ruminants of south Gujarat, India
- PMID: 37745222
- PMCID: PMC10516478
- DOI: 10.2478/helm-2023-0020
Morphological and molecular characterization of Haemonchus contortus isolated from the small ruminants of south Gujarat, India
Abstract
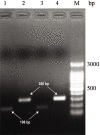
The successful design of strategic control measures against the blood-sucking gastrointestinal nematode, Haemonchus contortus in small ruminants can be facilitated by revealing its general features from morphology to the molecular level. In the south Gujarat region of India, a total of 2408 H. contortus were collected from 84 slaughtered sheep's abomasum, consisting of 347 males and 2061 females (1:6 ratio) (p<0.05). Furthermore, 726 H. contortus were collected from 61 goats, comprising 145 males and 581 females (1:4 ratio) (p<0.05). The male worms were approximately 12±0.06 mm long, while female worms were about 20±0.09 mm long. The vulvar morphotypes of the female worms were found to be 17.7% linguiform, 76.6 % knobbed/button (p<0.05), and 5.7 % smooth type, demonstrating common features of H. contortus. The nucleotide sequences of the Internal Transcribed Spacer 1 (ITS-1) of 165 bp or ITS-2 plus of 256 bp were aligned, and it was found that the genotypes of male and female specimens of either sheep or goat origin were identical, with a 100 % match. The present isolates shared >95 % and >94 % homology with published sequences of ITS-1 and ITS-2 plus of H. contortus, respectively, with more nucleotide transitions than transversions in the aligned sequences. The reconstructed phylogram of either ITS-1 or ITS-2 plus revealed two major clades, one for H. contortus and another for other nematodes, with Haemonchus placei showing its proximity with the clade of H. contortus. The study established the role of morphological and molecular features in identifying and differentiating H. contortus parasite at the local level.
Keywords: Haemonchus contortus; ITS; Molecular; PCR; Small ruminants; Vulvar morphology.
© 2023 B. Das et al., published by Sciendo.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Abdel-Hafez B.A., Badawy A.I.I., Hassanen E.A.A.. Morphology and molecular characterization of Haemonchus contortus from sheep at Sharkia Province, Egypt. Egypt Vet Med Soc Parasitol J. 2013;9:95–10.
-
- Abramatov M.B., Amirov O.O., Kuchboev A.E., Khalilov I.M., Abdurakhmanov I.Y.. Morphological and molecular characterization of Haemonchus contortus and H. placei (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) from Uzbekistan by sequences of the second internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA. Sci Parasitol. 2013;14(3):115–12.
-
- Akkari H., Gharbi M., Awadi S., Mohamed A.D., Kumsa B.. New sublinguiform vulvar flap of Haemonchus species in naturally infected domestic ruminants in Béja Abattoir, North Tunisia. Vet Arh. 2013a;83(3):281–29.
-
- Akkari H., Jebali J., Gharbi M., Mhadhbi M., Awadi S., Darghouth M.A.. Epidemiological study of sympatric Haemonchus species and genetic characterization of Haemonchus contortus in domestic ruminants in Tunisia. Vet Parasitol. 2013b;193(1–3):118–125. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.014. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
