The accordion technique enhances bone regeneration via angiogenesis factor in a rat distraction osteogenesis model
- PMID: 37745241
- PMCID: PMC10514895
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1259567
The accordion technique enhances bone regeneration via angiogenesis factor in a rat distraction osteogenesis model
Abstract
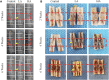
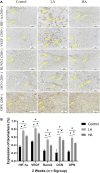
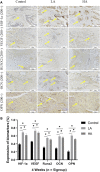
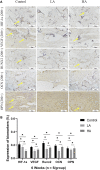
Objective: The purpose of this study was to observe the effect of the accordion technique (AT) during the distraction phase on chondrogenesis and bone regeneration in a rat femoral distraction osteogenesis (DO) model, and investigate its potential mechanism for reducing the total treatment time of DO. Methods: Fifty-four male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats that were specific-pathogen-free (SPF) were subjected to DO surgery on the right femur. The distraction rate was 0.5 mm/day for 10 days, following a latency period of 5 days. Rats were randomly divided into Control (no AT, n = 18), Group LA (low amplitude with AT, n = 18), and Group HA (high amplitude with AT, n = 18) according to different AT protocols in the distraction phase. Rats were respectively euthanized by anesthesia overdose at 2, 4 and 6 weeks of the consolidation phase, and the femurs were harvested. Digital radiography, micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), biomechanical tests, and histomorphological analysis were used to assess the quality of regenerated bone in the distraction area. Results: Digital radiographic, micro-CT, biomechanical tests, and histological analysis revealed an increase in early-stage callus formation (p < 0.05) and improved blood supply to the callus tissue in Group LA, as compared to both the Control and Group HA. The enhanced differentiation of fibrous and cartilaginous tissue into bone tissue was also observed in Group LA, leading to improved strength and stiffness (p < 0.05) of the regenerated bone at 6 weeks of the consolidation phase. The angiogenic (hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), p < 0.05) and osteogenic (runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), osteocalcin (OCN) and osteopontin (OPN), p < 0.05) biomarkers were higher expressed in Group LA at 2 and 4 weeks of consolidation phase, whereas decreased at 6 weeks of consolidation phase. Conclusion: The application of AT with low amplitude during the distraction phase can enhance chondrogenesis and bone regeneration by activating the angiogenesis factor pathway and upregulating the expression of osteogenic-related biomarkers such as HIF-1α, VEGF, RUNX2, OCN, and OPN.
Keywords: accordion maneuver; angiogenesis factor; bone regeneration; bone remodeling; distraction osteogenesis.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Wang, Yalikun, Ren and Yusufu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bezstarosti H., Metsemakers W. J., van Lieshout E., Voskamp L. W., Kortram K., McNally M. A., et al. (2021). Management of critical-sized bone defects in the treatment of fracture-related infection: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 141 (7), 1215–1230. 10.1007/s00402-020-03525-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

