This is a preprint.
Regulation of human interferon signaling by transposon exonization
- PMID: 37745311
- PMCID: PMC10515820
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.11.557241
Regulation of human interferon signaling by transposon exonization
Update in
-
Regulation of human interferon signaling by transposon exonization.Cell. 2024 Dec 26;187(26):7621-7636.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.11.016. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39672162 Free PMC article.
Abstract
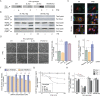
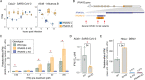
Innate immune signaling is essential for clearing pathogens and damaged cells, and must be tightly regulated to avoid excessive inflammation or autoimmunity. Here, we found that the alternative splicing of exons derived from transposable elements is a key mechanism controlling immune signaling in human cells. By analyzing long-read transcriptome datasets, we identified numerous transposon exonization events predicted to generate functional protein variants of immune genes, including the type I interferon receptor IFNAR2. We demonstrated that the transposon-derived isoform of IFNAR2 is more highly expressed than the canonical isoform in almost all tissues, and functions as a decoy receptor that potently inhibits interferon signaling including in cells infected with SARS-CoV-2. Our findings uncover a primate-specific axis controlling interferon signaling and show how a transposon exonization event can be co-opted for immune regulation.
Keywords: alternative splicing; innate immunity; transposable elements; type I IFN.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests: We have a patent application related to this work (PCT Application No. PCT/US2023/066767). Authors declare that they have no further competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Roelofs M.F., Wenink M.H., Brentano F., Abdollahi-Roodsaz S., Oppers-Walgreen B., Barrera P., van Riel P.L.C.M., Joosten L.A.B., Kyburz D., van den Berg W.B., et al. (2009). Type I interferons might form the link between Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3/7 and TLR4-mediated synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 1486–1493. 10.1136/ard.2007.086421. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
