This is a preprint.
Lupus IgA1 autoantibodies synergize with IgG to enhance pDC responses to RNA-containing immune complexes
- PMID: 37745328
- PMCID: PMC10515763
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.07.556743
Lupus IgA1 autoantibodies synergize with IgG to enhance pDC responses to RNA-containing immune complexes
Update in
-
Lupus IgA1 autoantibodies synergize with IgG to enhance plasmacytoid dendritic cell responses to RNA-containing immune complexes.Sci Transl Med. 2024 Jul 3;16(754):eadl3848. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adl3848. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38959329 Free PMC article.
Abstract
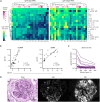
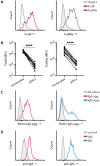
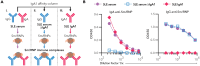
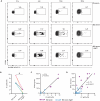
Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens are hallmarks of the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) where they contribute to pathogenesis. However, there remains a gap in our knowledge regarding how different isotypes of autoantibodies contribute to disease, including the production of the critical type I interferon (IFN) cytokines by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) in response to immune complexes (ICs). We focused on IgA, which is the second most prevalent isotype in serum, and along with IgG is deposited in glomeruli in lupus nephritis. Here, we show that individuals with SLE have IgA autoantibodies against most nuclear antigens, correlating with IgG against the same antigen. We investigated whether IgA autoantibodies against a major SLE autoantigen, Smith ribonucleoproteins (Sm/RNPs), play a role in IC activation of pDCs. We found that pDCs express the IgA-specific Fc receptor, FcαR, and there was a striking ability of IgA1 autoantibodies to synergize with IgG in RNA-containing ICs to generate robust pDC IFNα responses. pDC responses to these ICs required both FcαR and FcγRIIa, showing a potent synergy between these Fc receptors. Sm/RNP IC binding to and internalization by pDCs were greater when ICs contained both IgA1 and IgG. pDCs from individuals with SLE had higher binding of IgA1-containing ICs and higher expression of FcαR than pDCs from healthy control individuals. Whereas pDC FcαR expression correlated with blood ISG signature in SLE, TLR7 agonists, but not IFNα, upregulated pDC FcαR expression in vitro. Together, we show a new mechanism by which IgA1 autoantibodies contribute to SLE pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.H.B. is a Scientific Co-Founder and Scientific Advisory Board member of GentiBio, a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Neoleukin Therapeutics and Hotspot Therapeutics, and has past and current research projects sponsored by Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. She is a member of the Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Study Group, a partner of the Allen Institute for Immunology, and a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards for the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, and BMS Immunology. J.H.B also has a patent for tenascin-C autoantigenic epitopes in rheumatoid arthritis. J.A.H. has been a consultant for aTyr Pharma. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures

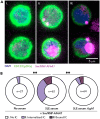
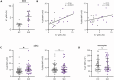
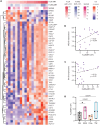
References
-
- Båve U., Magnusson M., Eloranta M.-L., Perers A., Alm G. V., Rönnblom L., FcγRIIa Is Expressed on Natural IFN-α-Producing Cells (Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells) and Is Required for the IFN-α Production Induced by Apoptotic Cells Combined with Lupus IgG. J. Immunol. 171, 3296–3302 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
