This is a preprint.
An explainable language model for antibody specificity prediction using curated influenza hemagglutinin antibodies
- PMID: 37745338
- PMCID: PMC10515799
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.11.557288
An explainable language model for antibody specificity prediction using curated influenza hemagglutinin antibodies
Update in
-
An explainable language model for antibody specificity prediction using curated influenza hemagglutinin antibodies.Immunity. 2024 Oct 8;57(10):2453-2465.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.022. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39163866 Free PMC article.
Abstract
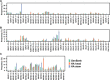
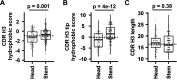
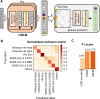
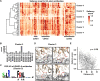
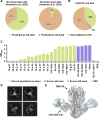
Despite decades of antibody research, it remains challenging to predict the specificity of an antibody solely based on its sequence. Two major obstacles are the lack of appropriate models and inaccessibility of datasets for model training. In this study, we curated a dataset of >5,000 influenza hemagglutinin (HA) antibodies by mining research publications and patents, which revealed many distinct sequence features between antibodies to HA head and stem domains. We then leveraged this dataset to develop a lightweight memory B cell language model (mBLM) for sequence-based antibody specificity prediction. Model explainability analysis showed that mBLM captured key sequence motifs of HA stem antibodies. Additionally, by applying mBLM to HA antibodies with unknown epitopes, we discovered and experimentally validated many HA stem antibodies. Overall, this study not only advances our molecular understanding of antibody response to influenza virus, but also provides an invaluable resource for applying deep learning to antibody research.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS N.C.W. consults for HeliXon. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
