This is a preprint.
Social Determinants of Genetics Referral and Completion Rates Among Child Neurology Patients
- PMID: 37745339
- PMCID: PMC10516043
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.12.23295450
Social Determinants of Genetics Referral and Completion Rates Among Child Neurology Patients
Update in
-
Association of Social Determinants of Health With Genetic Test Request and Completion Rates in Children With Neurologic Disorders.Neurology. 2025 Mar 11;104(5):e210275. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210275. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Neurology. 2025. PMID: 39937999
Abstract
Objective: To investigate clinical, social, and systems-level determinants predictive of genetics clinic referral and completion of genetics clinic visits among child neurology patients.
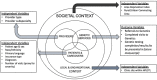
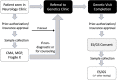
Methods: Electronic health record data were extracted from patients 0-18 years old who were evaluated in child neurology clinics at a single tertiary care institution between July 2018 to January 2020. Variables aligned with the Health Equity Implementation Framework. Referral and referral completion rates to genetics and cardiology clinics were compared among Black vs White patients using bivariate analysis. Demographic variables associated with genetics clinic referral and visit completion were identified using logistic regressions.
Results: In a cohort of 11,371 child neurology patients, 304 genetics clinic referrals and 82 cardiology clinic referrals were placed. In multivariate analysis of patients with Black or White ethnoracial identity (n=10,601), genetics clinic referral rates did not differ by race, but were significantly associated with younger age, rural address, neurodevelopmental disorder diagnosis, number of neurology clinic visits, and provider type. The only predictors of genetics clinic visit completion number of neurology clinic visits and race/ethnicity, with White patients being twice as likely as Black patients to complete the visit. Cardiology clinic referrals and visit completion did not differ by race/ethnicity.
Interpretation: Although race/ethnicity was not associated with differences in genetics clinic referral rates, White patients were twice as likely as Black patients to complete a genetics clinic visit after referral. Further work is needed to determine whether this is due to systemic/structural racism, differences in attitudes toward genetic testing, or other factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest The authors do not have any relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Manickam K, McClain MR, Demmer LA, et al. Exome and genome sequencing for pediatric patients with congenital anomalies or intellectual disability: an evidence-based clinical guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. Nov 2021;23(11):2029–2037. doi:10.1038/s41436-021-01242-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
