This is a preprint.
Uncoupling the TFIIH Core and Kinase Modules Leads To Misregulated RNA Polymerase II CTD Serine 5 Phosphorylation
- PMID: 37745343
- PMCID: PMC10515806
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.11.557269
Uncoupling the TFIIH Core and Kinase Modules Leads To Misregulated RNA Polymerase II CTD Serine 5 Phosphorylation
Abstract
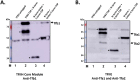
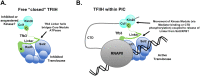
TFIIH is an essential transcription initiation factor for RNA polymerase II (RNApII). This multi-subunit complex comprises two modules that are physically linked by the subunit Tfb3 (MAT1 in metazoans). The TFIIH Core Module, with two DNA-dependent ATPases and several additional subunits, promotes DNA unwinding. The TFIIH Kinase Module phosphorylates Serine 5 of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNApII subunit Rpb1, a modification that coordinates exchange of initiation and early elongation factors. While it is not obvious why these two disparate activities are bundled into one factor, the connection may provide temporal coordination during early initiation. Here we show that Tfb3 can be split into two parts to uncouple the TFIIH modules. The resulting cells grow slower than normal, but are viable. Chromatin immunoprecipitation of the split TFIIH shows that the Core Module, but not the Kinase, is properly recruited to promoters. Instead of the normal promoter-proximal peak, high CTD Serine 5 phosphorylation is seen throughout transcribed regions. Therefore, coupling the TFIIH modules is necessary to localize and limit CTD kinase activity to early stages of transcription. These results are consistent with the idea that the two TFIIH modules began as independent functional entities that became connected by Tfb3 during early eukaryotic evolution.
Keywords: Biological Sciences: Biochemistry; Genetics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modulation of TFIIH-associated kinase activity by complex formation and its relationship with CTD phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II.Genes Cells. 2000 May;5(5):407-23. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00336.x. Genes Cells. 2000. PMID: 10886368
-
Kin28 is found within TFIIH and a Kin28-Ccl1-Tfb3 trimer complex with differential sensitivities to T-loop phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;22(5):1288-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.5.1288-1297.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11839796 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-shock inactivation of the TFIIH-associated kinase and change in the phosphorylation sites on the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Feb 15;25(4):694-700. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.4.694. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9016617 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II plays central roles in the integrated events of eucaryotic gene expression.J Biochem. 2007 May;141(5):601-8. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvm090. Epub 2007 Apr 3. J Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17405796 Review.
-
Two sides of the same coin: TFIIH complexes in transcription and DNA repair.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Apr 13;10:633-43. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.46. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20419276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vannini A., Cramer P., Conservation between the RNA Polymerase I, II, and III Transcription Initiation Machineries. Molecular Cell 45, 439–446 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Thomas M. C., Chiang C.-M., The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology 41, 105–178 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
