This is a preprint.
The white-footed deermouse, an infection-tolerant reservoir for several zoonotic agents, tempers interferon responses to endotoxin in comparison to the mouse and rat
- PMID: 37745581
- PMCID: PMC10515768
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543964
The white-footed deermouse, an infection-tolerant reservoir for several zoonotic agents, tempers interferon responses to endotoxin in comparison to the mouse and rat
Update in
- This article has been published with doi: 10.7554/eLife.90135.3 doi: 10.7554/eLife.90135.3
-
The infection-tolerant white-footed deermouse tempers interferon responses to endotoxin in comparison to the mouse and rat.Elife. 2024 Jan 9;12:RP90135. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90135. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38193896 Free PMC article.
Abstract
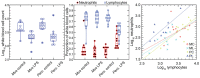
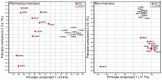
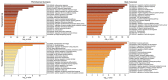
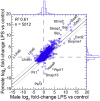
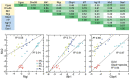
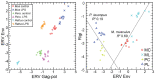
The white-footed deermouse Peromyscus leucopus, a long-lived rodent, is a key reservoir for agents of several zoonoses, including Lyme disease. While persistently infected, this deermouse is without apparent disability or diminished fitness. For a model for inflammation elicited by various pathogens, the endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to compare genome-wide transcription in blood by P. leucopus, Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus and adjusted for white cell concentrations. Deermice were distinguished from the mice and rats by LPS response profiles consistent with non-classical monocytes and alternatively-activated macrophages. LPS-treated P. leucopus, in contrast to mice and rats, also displayed little transcription of interferon-gamma and lower magnitude fold-changes in type 1 interferon-stimulated genes. This was associated with comparatively reduced transcription of endogenous retrovirus sequences and cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptors in the deermice. The results reveal a mechanism for infection tolerance in this species and perhaps other animal reservoirs for agents of human disease.
Keywords: endogenous retroviruses; innate immunity; interferon stimulated genes; interferon-gamma; lipopolysaccharide; pathogen recognition receptors; type 1 interferons.
Figures
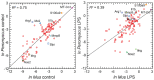
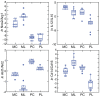
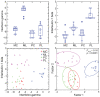
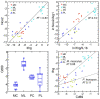

References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genet. 2000;25(1):25–9. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balderrama-Gutierrez G, Milovic A, Cook VJ, Islam MN, Zhang Y, Kiaris H, Belisle JT, Mortazavi A, Barbour AG. An infection-tolerant mammalian reservoir for several zoonotic agents broadly counters the inflammatory effects of endotoxin. mBio. 2021;12(2). Epub 20210413. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00588-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbour AG. Borreliaceae. In: Whitman WB, Rainey R, P. Kämpfe P, Trujillo M, Chun J, DeVos P, Hedlund B, Dedysh S, editors. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. 2018. p. 1–9. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, USA
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
