Treatment of multisegmental vertebral compression, burst fractures, and sandwich vertebra with severe osteoporosis using the PKP technique: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 37745651
- PMCID: PMC10511751
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1118891
Treatment of multisegmental vertebral compression, burst fractures, and sandwich vertebra with severe osteoporosis using the PKP technique: a case report and literature review
Abstract
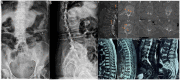
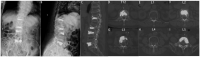
This study aimed to present a special case of treatment of a patient with multisegmental vertebral compression fracture, burst fracture, and sandwich vertebra and to review the literature on this condition. An 85 year-old female presented with severe low back pain but no radiating pain in the lower extremities. The patient was diagnosed with T12 and L5 vertebral compression fractures, fresh vertebral burst fractures in L2 and L3, and osteoporosis. The focus was on formulating a surgical treatment strategy. At the 12 month follow-up, no neurological deficits were observed, and the chosen surgical treatment approach yielded favorable clinical outcomes. A comprehensive literature review indicates that percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP) can effectively alleviate pain and ensure safety in managing osteoporotic vertebral burst fractures. While complications remain a theoretical risk, they can be mitigated through meticulous assessment, careful surgical procedures, and appropriate preventive measures. PKP is an effective and safe treatment modality for osteoporotic vertebral burst fractures. Conservative management of sandwich vertebrae can yield positive clinical outcomes, but regular anti-osteoporosis treatment is necessary.
Keywords: burst fracture; multisegmental vertebral compression fracture; osteoporosis; percutaneous kyphoplasty; sandwich vertebra.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Pang, Hai, Yang, Fan, Gao and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

