Predictive value of whole-brain CT perfusion combined with ABCD3 score for short-term secondary cerebral infarction after TIA
- PMID: 37745657
- PMCID: PMC10513042
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1244014
Predictive value of whole-brain CT perfusion combined with ABCD3 score for short-term secondary cerebral infarction after TIA
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the predictive value of Whole Brain CT Perfusion (WB-CTP) combined with the ABCD3 score in patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Methods: A total of 336 TIA patients with TIA underwent WB-CTP and ABCD3 score assessment within 48 h of admission. Spearman correlation test was performed to analyze the relationship between the degree of vascular stenosis, relative perfusion values, and ABCD3 score. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent risk factors for secondary cerebral infarction. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the predictive value of relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF), degree of vascular stenosis, ABCD3 score, and the WB-CTP-ABCD3 combined model for secondary cerebral infarction after TIA. Calibration curves and H-L tests were used to evaluate the predictive efficacy of the model.
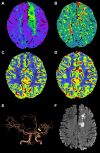
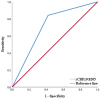
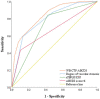
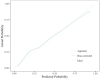
Results: Among the 336 TIA patients, 143 showed abnormal perfusion areas and 146 had responsible vessel stenosis. The degree of vascular stenosis, relative time-to-maximum (rTmax), and relative mean transit time (rMTT) were positively correlated with the ABCD3 score, while rCBF and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) were negatively correlated with the ABCD3 score. ROC curve analysis identified a cutoff value of 0.8205 for rCBF, with a sensitivity of 84.10% and specificity of 58.10% for distinguishing the cerebral infarction group from the non-cerebral infarction group. Furthermore, rCBF ≤ 0.8205, degree of vascular stenosis, and ABCD3 score > 6 were identified as independent risk factors for secondary cerebral infarction in TIA patients within 90 days in TIA patients. The AUC of the WB-CTP-ABCD3 combined model for predicting secondary cerebral infarction within 90 days was 0.836. The model risk was assessed by plotting calibration curves. The value of p for the H-L goodness of fit test was 0.366 (p > 0.05), which indicated that the difference between the obtained model and the perfect model were statistically insignificant.
Conclusion: The combined model of WB-CTP-ABCD3 shows promise as a valuable method for predicting secondary cerebral infarction within 90 days following TIA.
Keywords: ABCD3 score; CT perfusion; secondary cerebral infarction; transient ischemic attack; whole brain.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Chen and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, et al. . 2021 guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2021) 52:e364–467. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000375 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kelly PJ, Albers GW, Chatzikonstantinou A, de Marchis GM, Ferrari J, George P, et al. . Validation and comparison of imaging-based scores for prediction of early stroke risk after transient ischaemic attack: a pooled analysis of individual-patient data from cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. (2016) 15:1238–47. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30236-8, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kiyohara T, Kamouchi M, Kumai Y, Ninomiya T, Hata J, Yoshimura S, et al. . ABCD3 and ABCD3-I scores are superior to ABCD2 score in the prediction of short- and long-term risks of stroke after transient ischemic attack. Stroke. (2014) 45:418–25. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003077, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Merwick A, Albers GW, Amarenco P, Arsava EM, Ay H, Calvet D, et al. . Addition of brain and carotid imaging to the ABCD2 score to identify patients at early risk of stroke after transient ischaemic attack: a multicentre observational study. Lancet Neurol. (2010) 9:1060–9. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70240-4, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

