The use of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Hashimoto's encephalopathy: case based review
- PMID: 37745658
- PMCID: PMC10513043
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1243787
The use of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Hashimoto's encephalopathy: case based review
Abstract
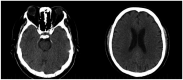
Background: Hashimoto's encephalopathy (HE) is a controversial immunological neuropsychiatric disease, with a poorly understood pathogenesis. It is characterized by symptoms of acute or subacute encephalopathy which usually occur in the presence of elevated levels of antithyroid antibodies. Even though it is also known as steroid responsive encephalopathy associated with autoimmune thyroiditis (SREAT), some cases appear to be steroid-resistant. This review examined whether treatment of Hashimoto's encephalopathy with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is associated with better clinical outcomes than the standard therapy. Additionally, we presented a case of a 59-year-old man who presented with severe neurological manifestations and was successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Methods: The online databases PubMed and EMBASE were searched.
Results: A total of 1,365 articles were identified. After the deletion of 112 duplicates, 1,253 studies were screened by evaluating the title and abstract, focusing on Hashimoto's encephalopathy cases where IVIG were used. 846 studies were excluded because they were not relevant to the topic or included pediatric population. Therefore, 407 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. The final analysis included 14 eligible articles after 393 were excluded (irrelevant texts, not written in English, full-text not available). In the majority of the selected case-reports, IVIG was associated with a good outcome, sometimes even with dramatic improvements in patient's status.
Conclusion: In last years, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy proved its utility in Hashimoto's encephalopathy's treatment, being a well tolerated therapy associated with remarkable improvement in patient's status. Further research is still needed in order to define the optimal treatment protocol for Hashimoto's encephalopathy and to establish if intravenous immunoglobulin can also be used as a first-line therapy, alone or in combination with steroids.
Keywords: Hashimoto’s encephalopathy; alpha-enolase; anti-thyroglobulin; anti-thyroid peroxidase; autoimmune encephalopathy; intravenous immunoglobulin.
Copyright © 2023 Şorodoc, Constantin, Asaftei, Lionte, Ceasovschih, Sîrbu, Haliga and Şorodoc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

