Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with urinary incontinence in elderly men: evidence based on NHANES 2007-2014
- PMID: 37745700
- PMCID: PMC10515204
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1215666
Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with urinary incontinence in elderly men: evidence based on NHANES 2007-2014
Abstract
Background: The correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and different sub-types of urinary incontinence in elderly men continues to be uncertain. Hence, we performed this research to evaluate whether serum 25(OH)D levels are correlated with urinary incontinence among elderly men.
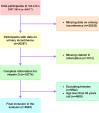
Methods: The present study incorporated the male population aged 50 years and above from four cycles of the NHANES database spanning from 2007 to 2014, for the purpose of analysis. The assessment of urinary incontinence was carried out through a correlation questionnaire, while standardized liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was adopted to quantify serum 25(OH)D. A weighted multi-factorial logistic regression analysis was carried out to ascertain and investigate any potential correlation that may exist between serum 25(OH)D and urinary incontinence in senior males.
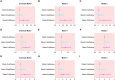
Results: Ultimately, a sum of 4663 elderly men were involved in our analysis. The outcomes of the univariable analysis illustrated that the group with vitamin D deficiency exhibited augmented odds of all three urinary incontinence types in comparison to the vitamin D-sufficient group. After accounting for age, race, and BMI, no appreciable variations in the outcomes were noticed. However, after accounting for all covariates, only SUI (OR = 1.677; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.074-2.618) and MUI (OR = 1.815; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.010-3.260) demonstrated statistical significance.
Conclusion: Decreased serum 25(OH)D levels were connected with stress urinary incontinence and mixed urinary incontinence in elderly men.
Keywords: 25-hydroxyvitamin D; NHANES; elderly men; urinary incontinence; vitamin D deficiency.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Xu, Zhou, Hao, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical