HDAC1 is Involved in Neuroinflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in Stroke Pathogenesis
- PMID: 37745794
- PMCID: PMC10516226
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S416239
HDAC1 is Involved in Neuroinflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in Stroke Pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Stroke is a common cause of disability and mortality worldwide; however, effective therapy remains limited. In stroke pathogenesis, ischemia/reperfusion injury triggers gliosis and neuroinflammation that further activates matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), thereby damaging the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Increased BBB permeability promotes macrophage infiltration and brain edema, thereby worsening behavioral outcomes and prognosis. Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is a repressor of epigenomic gene transcription and participates in DNA damage and cell cycle regulation. Although HDAC1 is deregulated after stroke and is involved in neuronal loss and DNA repair, its role in neuroinflammation and BBB damage remains unknown.
Methods: The rats with cerebral ischemia were evaluated in behavioral outcomes, levels of inflammation in gliosis and cytokines, and BBB damage by using an endothelin-1-induced rat model with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
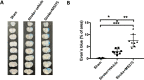
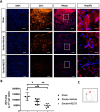
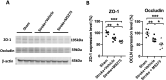
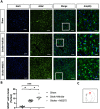
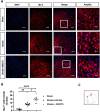
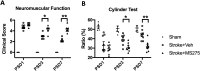
Results: The results revealed that HDAC1 dysfunction could promote BBB damage through the destruction of tight junction proteins, such as ZO-1 and occludin, after stroke in rats. HDAC1 inhibition also increased the levels of astrocyte and microglial gliosis, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, lactate dehydrogenase, and reactive oxygen species, further triggering MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. Moreover, modified neurological severity scores for the cylinder test revealed that HDAC1 inhibition deteriorated behavioral outcomes in rats with cerebral ischemia.
Discussion: HDAC1 plays a crucial role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced neuroinflammation and BBB damage, thus indicating its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: HDAC1; IL-1β; ROS; TNF-α; blood-brain barrier; cylinder test; mNSS; stroke.
© 2023 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

