A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- PMID: 37745978
- PMCID: PMC10512444
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2023-0773
A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
Abstract
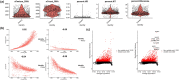
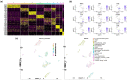
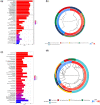
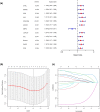
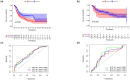
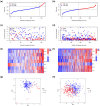
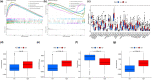
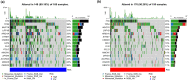
Bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA) is one of the most common cancer-related deaths in the world, along with high mortality. Due to the difficult detection of early symptoms, the treatment for this disease is still dissatisfactory. Thus, the current research hotspot is beginning to focus on the immune microenvironment in this disease, aiming to provide guidance for diagnosis and treatment. In this study, the single-cell RNA sequencing data downloaded from the gene expression omnibus database was used to classify the immune cells of BLCA. And the final seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes associated with BLCA prognosis (HSPA2, A2M, JUN, PDGFRB, GBP2, LGALS1, and GAS6) were screened out, and then used for constructing the prognostic model against BLCA based on the Cox and LASSO regression analysis. Satisfactorily, the model could efficiently evaluate the overall survival of BLCA and had the potential to be applied for the clinic treatment. Moreover, we also revealed that the difference in immune infiltration levels and gene mutation might account for the diverse prognosis in BLCA patients. In a word, our findings provided a novel insight for designing efficient immunotherapies for BLCA.
Keywords: bladder urothelial carcinoma; immune microenvironment; prognosis; single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wullweber A, Strick R, Lange F. Bladder tumor subtype commitment occurs in carcinoma in situ driven by key signaling pathways including ECM remodeling. Cancer Res. 2021;81:1552–66. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Nadal R, Bellmunt J. Management of metastatic bladder cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;76:10–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
