Innate and adaptive AAV-mediated immune responses in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 37746243
- PMCID: PMC10512012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.06.002
Innate and adaptive AAV-mediated immune responses in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
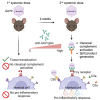
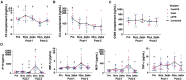
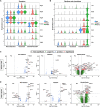
High systemic doses of adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have been associated with immune-related serious adverse events (SAEs). Although AAV was well tolerated in preclinical models, SAEs were observed in clinical trials, indicating the need for improved preclinical models to understand AAV-induced immune responses. Here, we show that mice dual-dosed with AAV9 at 4-week intervals better recapitulate aspects of human immunity to AAV. In the model, anti-AAV9 immunoglobulin G (IgGs) increased in a linear fashion between the first and second AAV administrations. Complement activation was only observed in the presence of high levels of both AAV and anti-AAV IgG. Myeloid-derived pro-inflammatory cytokines were significantly induced in the same pattern as complement activation, suggesting that myeloid cell activation to AAV may rely on the presence of both AAV and anti-AAV IgG complexes. Single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells confirmed that activated monocytes were a primary source of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which were significantly increased after a second AAV9 exposure. The same activated monocyte clusters expressed both Fcγ and complement receptors, suggesting that anti-AAV-mediated activation of myeloid cells through Fcγ receptors and/or complement receptors is one mechanism by which anti-AAV antigen complexes may prime antigen-presenting cells and amplify downstream immunity.
Keywords: Luminex; adaptive immunity; adeno-associated virus; innate immunity; muscular dystrophy; single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.S., A.D.P., and C.S.Y. are co-founders of MyoGene Bio, a startup spun out of UCLA developing gene editing therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Figures



References
-
- Chand D.H., Zaidman C., Arya K., Millner R., Farrar M.A., Mackie F.E., Goedeker N.L., Dharnidharka V.R., Dandamudi R., Reyna S.P. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Following Onasemnogene Abeparvovec for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Case Series. J. Pediatr. 2021;231:265–268. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.11.054. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R44 AR075469/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046911/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR064327/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR057230/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS120060/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS114918/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR052646/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040864/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS117912/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

