The role of breastfeeding in breast cancer prevention: a literature review
- PMID: 37746260
- PMCID: PMC10512942
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1257804
The role of breastfeeding in breast cancer prevention: a literature review
Abstract
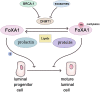
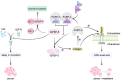
Breast cancer stands as the most prevalent malignancy globally. Despite the array of treatment options, its mortality rate continues to rise annually. Thus, reevaluation of factors directly linked to breast cancer emergence is imperative, alongside the development of more effective preventive measures. Estrogen levels, profoundly tied to reproduction, play a pivotal role in breast cancer development. Speculation centers on the potential of breastfeeding to mitigate cancer risk in women. However, the precise mechanism remains elusive. Breastfeeding is a modifiable reproductive factor extensively studied. Studies highlight a direct connection between lack of breastfeeding and breast cancer emergence, potentially linked to DNA methyltransferase expression alteration, aberrant methylation levels, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, cellular microenvironment, and oncogenes. This study reviews recent mechanisms underlying breastfeeding's role in reducing breast cancer incidence.
Keywords: breast cancer; breast involution; breastfeeding; mechanism; methylation.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Jiang and Geng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond Milk and Nurture: Breastfeeding's Powerful Impact on Breast Cancer.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024 Jun 13;84(6):541-554. doi: 10.1055/a-2313-0637. eCollection 2024 Jun. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024. PMID: 38884025 Free PMC article.
-
Breastfeeding's protective role in alleviating breast cancer burden: a comprehensive review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Mar 5;86(5):2805-2811. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001914. eCollection 2024 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38694322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the profound link: Breastfeeding's impact on alleviating the burden of breast cancer - A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 12;103(15):e37695. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037695. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38608095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abrupt involution induces inflammation, estrogenic signaling, and hyperplasia linking lack of breastfeeding with increased risk of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 17;21(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1163-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31315645 Free PMC article.
-
A methylation signature at the CpG island promoter of estrogen receptor beta (ER-β) in breasts of women may be an early footmark of lack of breastfeeding and nulliparity.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Feb;218:153328. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153328. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33422777
Cited by
-
Association between breastfeeding, mammographic density, and breast cancer risk: a review.Int Breastfeed J. 2024 Sep 16;19(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13006-024-00672-7. Int Breastfeed J. 2024. PMID: 39285438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breastfeeding in primiparous women with congenital heart disease - a register study.Int Breastfeed J. 2024 Mar 20;19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13006-024-00627-y. Int Breastfeed J. 2024. PMID: 38509505 Free PMC article.
-
Time to breastfeeding cessation and its predictors among mothers of index children aged 2-3 years in Bedele Town, Southwest Ethiopia: a community-based retrospective follow-up study.BMJ Public Health. 2025 Feb 6;3(1):e000573. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2023-000573. eCollection 2025. BMJ Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40017948 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of Breastfeeding and Risk Reduction of Breast Cancer among Mothers Who Have Ever Breastfed: A Case-Control Study Conducted in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia.Breast J. 2024 Sep 21;2024:1987378. doi: 10.1155/2024/1987378. eCollection 2024. Breast J. 2024. PMID: 39742364 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Milk and Nurture: Breastfeeding's Powerful Impact on Breast Cancer.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024 Jun 13;84(6):541-554. doi: 10.1055/a-2313-0637. eCollection 2024 Jun. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2024. PMID: 38884025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer . Breast cancer and breastfeeding: collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50302 women with breast cancer and 96973 women without the disease. Lancet (2002) 360(9328):187–95. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)09454-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

