Synergism of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl with ErbB receptors mediates resistance to regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37746265
- PMCID: PMC10514905
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1238883
Synergism of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl with ErbB receptors mediates resistance to regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients at advanced stages receive immunotherapy or treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as Sorafenib (Sora) or Lenvatinib in frontline as well as Regorafenib (Rego) or Cabozantinib in second-line. A major hindrance of TKI therapies is the development of resistance, which renders drug treatment futile and results in HCC progression.
Methods: In this study, we addressed the impact of the receptor tyrosine kinase Axl binding to its ligand Gas6 in acquiring refractoriness to TKIs. The initial responses of Axl-positive and Axl-negative cell lines to different TKIs were assessed. Upon inducing resistance, RNA-Seq, gain- and loss-of-function studies were applied to understand and intervene with the molecular basis of refractoriness. Secretome analysis was performed to identify potential biomarkers of resistance.
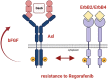
Results: We show that HCC cells exhibiting a mesenchymal-like phenotype were less sensitive to drug treatment, linking TKI resistance to changes in epithelial plasticity. Gas6/Axl expression and activation were upregulated in Rego-resistant HCC cells together with the induction of ErbB receptors, whereas HCC cells lacking Axl failed to stimulate ErbBs. Treatment of Rego-insensitive HCC cells with the pan-ErbB family inhibitor Afatinib rather than with Erlotinib blocking ErbB1 reduced cell viability and clonogenicity. Genetic intervention with ErbB2-4 but not ErbB1 confirmed their crucial involvement in refractoriness to Rego. Furthermore, Rego-resistant HCC cells secreted basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) depending on Axl expression. HCC patients treated with Sora in first-line and with Rego in second-line displayed elevated serum levels of bFGF, emphasizing bFGF as a predictive biomarker of TKI treatment.
Discussion: Together, these data suggest that the inhibition of ErbBs is synthetic lethal with Rego in Axl-expressing HCC cells, showing a novel vulnerability of HCC.
Keywords: Axl; ErbB; GAS6; Regorafenib; bFGF; hepatocellular carcinoma; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Breitenecker, Hedrich, Pupp, Chen, Řezníčková, Ortmayr, Huber, Weber, Balcar, Pinter and Mikulits.
Conflict of interest statement
MP served as a speaker and/or consultant and/or advisory board member for Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Ipsen, Lilly, MSD, and Roche, and received travel support from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PRAME Is a Novel Target of Tumor-Intrinsic Gas6/Axl Activation and Promotes Cancer Cell Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 22;15(9):2415. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092415. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173882 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of upregulated Rho GTPase activating protein 12 causing resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):4244-4263. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i10.4244. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39473957 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor tissue and plasma levels of AXL and GAS6 before and after tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Oct;10(10):1928-1935. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13166. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31419057 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Etiology and Current and Future Drugs.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Mar-Apr;9(2):221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31024205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AXL and MET in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Literature Review.Liver Cancer. 2022 Feb 10;11(2):94-112. doi: 10.1159/000520501. eCollection 2022 Apr. Liver Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35634427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GAS6/TAM Axis as Therapeutic Target in Liver Diseases.Semin Liver Dis. 2024 Feb;44(1):99-114. doi: 10.1055/a-2275-0408. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Semin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 38395061 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Clinical Implications and Potential Strategies to Overcome the Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;16(23):3944. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233944. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic advances of targeting receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Aug 14;9(1):201. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01899-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39138146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

