Rare case of pediatric trauma with hepatic injury managed using gel-foam embolization: a case report
- PMID: 37746525
- PMCID: PMC10516522
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjad522
Rare case of pediatric trauma with hepatic injury managed using gel-foam embolization: a case report
Abstract
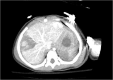
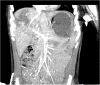
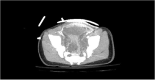
Nonoperative management for hepatic injuries requires observation and supportive care in the case of hemodynamically stable patients. If there is active bleeding on presentation, hepatic artery embolization is an option to achieve hemostasis in the acute setting. Although interventional radiology procedures are well documented in adults, there is limited literature regarding these procedures in the pediatric population. In this report, we present a case of a pediatric patient who sustained blunt abdominal trauma, resulting in a grade IV liver injury. Treatment involved fluoroscopically guided right hepatic segmental arterial gel-foam embolization.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. © The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complications of nonoperative management of pediatric blunt hepatic injury: Diagnosis, management, and outcomes.J Trauma. 2006 Aug;61(2):334-9. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000197605.27190.2c. J Trauma. 2006. PMID: 16917447
-
Gastric Artery Injury Due to Blunt Abdominal Trauma.Cureus. 2023 Dec 6;15(12):e50018. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50018. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38186483 Free PMC article.
-
Staged laparotomies based on the damage control principle to treat hemodynamically unstable grade IV blunt hepatic injury in an eight-year-old girl.Surg Case Rep. 2016 Dec;2(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s40792-016-0264-0. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Surg Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27854071 Free PMC article.
-
Update: Splenic Artery Embolization in Blunt Abdominal Trauma.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2020 Mar;37(1):97-102. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3401845. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32139975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma is the treatment of choice for hemodynamically stable patients. Results of a prospective trial.Ann Surg. 1995 Jun;221(6):744-53; discussion 753-5. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199506000-00013. Ann Surg. 1995. PMID: 7794078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stylianos S. Compliance with evidence-based guidelines in children with isolated spleen or liver injury: a prospective study. J Pediatr Surg 2002;37:453–6. - PubMed
-
- Coimbra R, Hoyt DB, Engelhart S. et al. Nonoperative management reduces the overall mortality of grades 3 and 4 blunt liver injuries. Int Surg 2006;91:251–7. - PubMed
-
- Nellensteijn D, Porte RJ, van Zuuren W. et al. Paediatric blunt liver trauma in a Dutch level 1 trauma center. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2009;19:358–61. - PubMed
-
- Miyayama S, Yamakado K, Anai H. et al. Guidelines on the use of gelatin sponge particles in embolotherapy. Jpn J Radiol 2014;32:242–50. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources