Successful catheter ablation for verapamil-sensitive idiopathic left ventricular tachycardia guided by dual post-QRS wave P1 potentials after catheter-induced mechanical block
- PMID: 37746557
- PMCID: PMC10511895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2023.07.002
Successful catheter ablation for verapamil-sensitive idiopathic left ventricular tachycardia guided by dual post-QRS wave P1 potentials after catheter-induced mechanical block
Keywords: Bump phenomenon; Catheter-induced mechanical block; Late P1 potential; Playback ablation; Verapamil-sensitive left fascicular ventricular tachycardia.
Figures
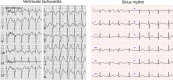
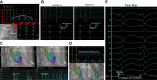
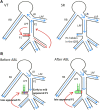
References
-
- Zipes D.P., Foster P.R., Troup P.J., Pedersen D.H. Atrial induction of ventricular tachycardia: reentry versus triggered automaticity. Am J Cardiol. 1979;44:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Klein G.J., Millman P.J., Yee R. Recurrent ventricular tachycardia responsive to verapamil. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1984;7:938–948. - PubMed
-
- Okumura K., Matsuyama K., Miyagi H., Tsuchiya T., Yasue H. Entrainment of idiopathic ventricular tachycardia of left ventricular origin with evidence for reentry with an area of slow conduction and effect of verapamil. Am J Cardiol. 1988;62:727–732. - PubMed
-
- Nogami A., Naito S., Tada H., et al. Demonstration of diastolic and presystolic Purkinje potentials as critical potentials in a macroreentry circuit of verapamil-sensitive idiopathic left ventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:811–823. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q., Shehata M., Jiang R., et al. Macroreentrant loop in ventricular tachycardia from the left posterior fascicle: new implications for mapping and ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016;9 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

