Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio predicts overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37746650
- PMCID: PMC10514720
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i9.1662
Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio predicts overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) has been found to be of prognostic significance for several types of malignant tumors. However, less is known about the association between FAR and survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
Aim: To explore the association between FAR and prognosis and survival in patients with HCC.
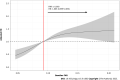
Methods: A total of 366 histologically confirmed HCC patients diagnosed between 2013 and 2018 in a provincial cancer hospital in southwestern China were retrospectively selected. Relevant data were extracted from the hospital information system. The optimal cutoff for baseline serum FAR measured upon disease diagnosis was established using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models were used to determine the crude and adjusted associations between FAR and the overall survival (OS) of the HCC patients while controlling for various covariates. The restricted cubic spline (RCS) was applied to estimate the dose-response trend in the FAR-OS association.
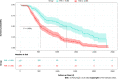
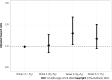
Results: The optimal cutoff value for baseline FAR determined by the ROC was 0.081. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards model revealed that a lower baseline serum FAR level was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio of 2.43 (95% confidence interval: 1.87-3.15) in the OS of HCC patients, with identifiable dose-response trend in the RCS. Subgroup analysis showed that this FAR-OS association was more prominent in HCC patients with a lower baseline serum aspartate aminotransferase or carbohydrate antigen 125 level.
Conclusion: Serum FAR is a prominent prognostic indicator for HCC. Intervention measures aimed at reducing FAR might result in survival benefit for HCC patients.
Keywords: Cox proportional hazards model; Fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Overall survival; Survival analysis.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Inflammation-Based Prognostic Score: The Fibrinogen/Albumin Ratio Predicts Prognoses of Patients after Curative Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Immunol Res. 2018 May 22;2018:4925498. doi: 10.1155/2018/4925498. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30027102 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio predicts the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma subjected to hepatectomy.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 May 23;22(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02328-4. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35606690 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of pretreatment albumin/globulin ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Aug 24;9:5317-28. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S109736. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27601923 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase to albumin ratio combined with aspartate aminotransferase to lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 25;99(48):e23339. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023339. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33235099 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinogen/albumin ratio as a promising predictor of platinum response and survival in ovarian clear cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jan 21;22(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09204-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35062908 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Aug 24;22(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03506-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39182155 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) in patients with pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 11;14:1465279. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1465279. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39723376 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio in patients with esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jun 23;23(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03886-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40551119 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2530689. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2530689. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40650392 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of serum albumin levels on cancer survival: a prospective cohort study.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 4;14:1323192. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1323192. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38500655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Hassanipour S, Vali M, Gaffari-Fam S, Nikbakht HA, Abdzadeh E, Joukar F, Pourshams A, Shafaghi A, Malakoutikhah M, Arab-Zozani M, Salehiniya H, Mansour-Ghanaei F. The survival rate of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asian countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EXCLI J. 2020;19:108–130. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohammadian M, Mahdavifar N, Mohammadian-Hafshejani A, Salehiniya H. Liver cancer in the world: epidemiology, incidence, mortality and risk factors. World Cancer Res J. 2018;5:e1082.
-
- Zhang CH, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Fan J, Gao Q. Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Liver Int. 2022;42:2029–2041. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

