Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease
- PMID: 37746665
- PMCID: PMC10511835
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.363
Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease
Abstract
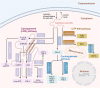
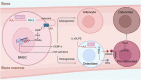
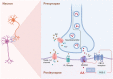
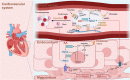
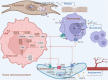
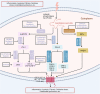
Arachidonic acid (AA), an n-6 essential fatty acid, is a major component of mammalian cells and can be released by phospholipase A2. Accumulating evidence indicates that AA plays essential biochemical roles, as it is the direct precursor of bioactive lipid metabolites of eicosanoids such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acid obtained from three distinct enzymatic metabolic pathways: the cyclooxygenase pathway, lipoxygenase pathway, and cytochrome P450 pathway. AA metabolism is involved not only in cell differentiation, tissue development, and organ function but also in the progression of diseases, such as hepatic fibrosis, neurodegeneration, obesity, diabetes, and cancers. These eicosanoids are generally considered proinflammatory molecules, as they can trigger oxidative stress and stimulate the immune response. Therefore, interventions in AA metabolic pathways are effective ways to manage inflammatory-related diseases in the clinic. Currently, inhibitors targeting enzymes related to AA metabolic pathways are an important area of drug discovery. Moreover, many advances have also been made in clinical studies of AA metabolic inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Herein, we review the discovery of AA and focus on AA metabolism in relation to health and diseases. Furthermore, inhibitors targeting AA metabolism are summarized, and potential clinical applications are discussed.
Keywords: arachidonic acid; bioactive lipid metabolites; organ homeostasis; targeted therapy.
© 2023 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Saini RK, Keum YS. Omega‐3 and omega‐6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: dietary sources, metabolism, and significance—a review. Life Sci. 2018;203:255‐267. - PubMed
-
- Lewkowitsch J. Chemical technology and analysis of oils, fats and waxes. 5th ed., Macmillan Company, New York, 1913.
-
- Mowry DT, Brode WR, Brown JB. Studies on the chemistry of the fatty acids: x. The structure of arachidonic acid as evidenced by oxidative degradation and selective hydrogenation. J Biol Chem. 1942;142(2):679‐691.
-
- Badimon L, Vilahur G, Rocca B, Patrono C. The key contribution of platelet and vascular arachidonic acid metabolism to the pathophysiology of atherothrombosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(9):2001‐2015. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
