4-Phenylbutyrate promoted wild-type γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor trafficking, reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress, and mitigated seizures in Gabrg2+/Q390X mice associated with Dravet syndrome
- PMID: 37746768
- PMCID: PMC10842976
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.17779
4-Phenylbutyrate promoted wild-type γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor trafficking, reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress, and mitigated seizures in Gabrg2+/Q390X mice associated with Dravet syndrome
Abstract
Objective: γ-Aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA ) receptor subunit gene mutations are major causes of various epilepsy syndromes, including severe kinds such as Dravet syndrome. Although the GABAA receptor is a major target for antiseizure medications, treating GABAA receptor mutations with receptor channel modulators is ineffective. Here, we determined the effect of a novel treatment with 4-phenylbutyrate (PBA) in Gabrg2+/Q390X knockin mice associated with Dravet syndrome.
Methods: We used biochemistry in conjunction with differential tagging of the wild-type and the mutant alleles, live brain slice surface biotinylation, microsome isolation, patch-clamp whole-cell recordings, and video-monitoring synchronized electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings in Gabrg2+/Q390X mice to determine the effect of PBA in vitro with recombinant GABAA receptors and in vivo with knockin mice.
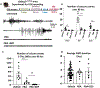
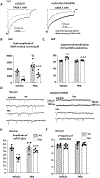
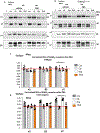
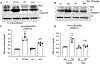
Results: We found that PBA reduced the mutant γ2(Q390X) subunit protein aggregates, enhanced the wild-type GABAA receptor subunits' trafficking, and increased the membrane expression of the wild-type receptors. PBA increased the current amplitude of GABA-evoked current in human embryonic kidney 293T cells and the neurons bearing the γ2(Q390X) subunit protein. PBA also proved to reduce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress caused by the mutant γ2(Q390X) subunit protein, as well as mitigating seizures and EEG abnormalities in the Gabrg2+/Q390X mice.
Significance: This research has unveiled a promising and innovative approach for treating epilepsy linked to GABAA receptor mutations through an unconventional antiseizure mechanism. Rather than directly modulating the affected mutant channel, PBA facilitates the folding and transportation of wild-type receptor subunits to the cell membrane and synapse. Combining these findings with our previous study, which demonstrated PBA's efficacy in restoring GABA transporter 1 (encoded by SLC6A1) function, we propose that PBA holds significant potential for a wide range of genetic epilepsies. Its ability to target shared molecular pathways involving mutant protein ER retention and impaired protein membrane trafficking suggests broad application in treating such conditions.
Keywords: 4-phenylbutyrate; ER stress; GABAA receptors; Gabrg2+/Q390X knockin mice; epilepsy.
© 2023 International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpressing wild-type γ2 subunits rescued the seizure phenotype in Gabrg2+/Q390X Dravet syndrome mice.Epilepsia. 2017 Aug;58(8):1451-1461. doi: 10.1111/epi.13810. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28586508 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperones and Mutant Protein Degradation in GABRG2(Q390X) Associated with Genetic Epilepsy with Febrile Seizures Plus and Dravet Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4601. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094601. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731820 Free PMC article.
-
Altered GABAA receptor expression in brainstem nuclei and SUDEP in Gabrg2(+/Q390X) mice associated with epileptic encephalopathy.Epilepsy Res. 2016 Jul;123:50-4. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Epilepsy Res. 2016. PMID: 27131289 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenic Basis for GABRG2 Mutations Associated With a Spectrum of Epilepsy Syndromes, From Generalized Absence Epilepsy to Dravet Syndrome.JAMA Neurol. 2016 Aug 1;73(8):1009-16. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0449. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27367160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutant GABA(A) receptor subunits in genetic (idiopathic) epilepsy.Prog Brain Res. 2014;213:55-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63326-2.00003-X. Prog Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 25194483 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteostasis regulation of GABAA receptors in neuronal function and disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 May;186:117992. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.117992. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40112516 Free PMC article. Review.

