Copper(II)-Catalyzed Three-Component Arylation/Hydroamination Cascade from Allyl Alcohol: Access to 1-Aryl-2-sulfonylamino-propanes
- PMID: 37747795
- PMCID: PMC10563128
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c01536
Copper(II)-Catalyzed Three-Component Arylation/Hydroamination Cascade from Allyl Alcohol: Access to 1-Aryl-2-sulfonylamino-propanes
Abstract
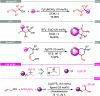
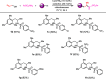
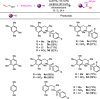
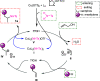
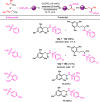
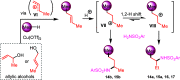
A new straightforward approach to 1-aryl-2-aminopropanes using easily accessible substrates has been developed. Simple allyl alcohol is shown to be an ideal synthetic equivalent of the C3 propane-1,2-diylium bis-cation synthon in three-component cascade reactions with arenes and sulfonamide nucleophiles to regioselectively afford 1-aryl-2-aminopropanes. The reaction is catalyzed by Cu(OTf)2 and is expected to involve a Friedel-Crafts-type allylation of the arene, followed by hydroamination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pelletier S. W.Chemistry of Alkaloids; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, 1970.
- Leake C. D.The Amphetamines: Their Actions and Uses; Charles C. Thomas Co.: Springfield, 1958.
- Testa B.; Salvesen B. J. Quantitative structure-activity relationships in drug metabolism and disposition. Pharmacokinetics of N-substituted amphetamines in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 497–501. 10.1002/jps.2600690505. - DOI - PubMed
- Jian-min C.; Zhi-yuan W.; Shi-xuan W.; Rui S.; Rui S.; Ning W.; Ning W.; Jin L. Effects of Lisdexamfetamine, a Prodrug of D-Amphetamine, on Locomotion, Spatial Cognitive Processing and Neurochemical Profiles in Rats: A Comparison With Immediate-Release Amphetamine. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 88557410.3389/fpsyt.2022.885574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Nieddu M.; Baralla E.; Pasciu V.; Rimoli M. G.; Boatto G. Cross-reactivity of commercial immunoassays for screening of new amphetamine designer drugs. A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 218, 11486810.1016/j.jpba.2022.114868. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imm S.; Bahn S.; Neubert L.; Neumann H.; Beller M. An Efficient and General Synthesis of Primary Amines by Ruthenium-Catalyzed Amination of Secondary Alcohols with Ammonia. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8126–8129. 10.1002/anie.201002576. - DOI - PubMed
- Muñoz L.; Rodriguez A. M.; Rosell G.; Bosch M. P.; Guerrero A. Enzymatic enantiomeric resolution of phenylethylamines structurally related to amphetamine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 8171–8177. 10.1039/c1ob06251d. - DOI - PubMed
- Jagadeesh R. V.; Murugesan K.; Alshammari A. S.; Neumann H.; Pohl M.-M.; Radnik J.; Beller M. MOF-Derived cobalt nanoparticles catalyze a general synthesis of amine. Science 2017, 358, 326–332. 10.1126/science.aan6245. - DOI - PubMed
- González-Martínez D.; Gotor V.; Gotor-Fernández V. Stereoselective Synthesis of 1-Arylpropan-2-amines from Allylbenzenes through a Wacker-Tsuji Oxidation-Biotransamination Sequential Process. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 2582–2593. 10.1002/adsc.201900179. - DOI
- Albarrán-Velo J.; Gotor-Fernández V.; Lavandera I. Markovnikov Wacker-Tsuji Oxidation of Allyl(hetero)arenes and Application in a One-Pot Photo-Metal-Biocatalytic Approach to Enantioenriched Amines and Alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 4096–4108. 10.1002/adsc.202100351. - DOI
-
- Griffith R. C.; Gentile R. J.; Davidson T. A.; Scott F. L. Convenient One-Step Synthesis of N-Substituted a-Methylphenylamines via Aminomercuration-Demercuration. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 3580–3583. 10.1021/jo01334a031. - DOI
- Hartung C. G.; Breindl C.; Tillack A.; Beller M. A Base-Catalyzed Domino-Isomerization-Hydroamination Reaction - A New Synthetic Route to Amphetamines. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 5157–5162. 10.1016/S0040-4020(00)00436-1. - DOI
- Utsunomiya M.; Hartwig J. F. Ruthenium-catalyzed anti-markovnikov hydroamination of vinylarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2702–2703. 10.1021/ja031542u. - DOI - PubMed
- Jaspers D.; Kubiak R.; Doye S. Recyclable Gallium as Catalyst Precursor for a Convenient and Solvent-Free Method for the Intermolecular Addition of Sulfonamides to Alkenes. Synlett 2010, 8, 1268–1272.
- Giner X.; Nájera C.; Kovács G.; Lledós A.; Ujaque G. Gold versus Silver-Catalyzed Intermolecular Hydroaminations of Alkenes and Dienes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 3451–3466. 10.1002/adsc.201100478. - DOI
-
- Foschi F.; Loro C.; Sala R.; Oble J.; Lo Presti L.; Beccalli E. M.; Poli G.; Broggini G. Intramolecular Aminoazidation of Unactivated Terminal Alkenes by Palladium-Catalyzed Reactions with Hydrogen Peroxide as the Oxidant. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 1402–1406. 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00010. - DOI - PubMed
- Giofrè S.; Loro C.; Molteni L.; Castellano C.; Contini A.; Nava D.; Broggini G.; Beccalli E. M. Copper(II)-Catalyzed Aminohalogenation of Alkynyl Carbamates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1750–1757. 10.1002/ejoc.202100202. - DOI
- Loro C.; Molteni L.; Papis M.; Beccalli E. M.; Nava D.; Lo Presti L.; Brenna S.; Colombo G.; Foschi F.; Broggini G. Direct Synthesis of Fluorescent Oxazolo-phenoxazines by Copper-Catalyzed/Hypervalent Iodine(III)-Mediated Dimerization/Cyclization of 2-Benzylamino-phenols. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 1032–1042. 10.1021/acs.joc.1c02329. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loro C.; Oble J.; Foschi F.; Papis M.; Beccalli E. M.; Giofrè S.; Poli G.; Broggini G. Acid-mediated decarboxylative C-H coupling between arenes and O-allyl carbamates. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1711–1718. 10.1039/D2QO00114D. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

