Variable microbiomes between mosquito lines are maintained across different environments
- PMID: 37747880
- PMCID: PMC10553814
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011306
Variable microbiomes between mosquito lines are maintained across different environments
Abstract
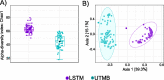
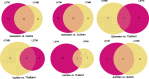
The composition of the microbiome is shaped by both environment and host in most organisms, but in the mosquito Aedes aegypti the role of the host in shaping the microbiome is poorly understood. Previously, we had shown that four lines of Ae. aegypti harbored different microbiomes when reared in the same insectary under identical conditions. To determine whether these lines differed from each other across time and in different environments, we characterized the microbiome of the same four lines of Ae. aegypti reared in the original insectary and at another institution. While it was clear that the environment influenced the microbiomes of these lines, we did still observe distinct differences in the microbiome between lines within each insectary. Clear differences were observed in alpha diversity, beta diversity, and abundance of specific bacterial taxa. To determine if the line specific differences in the microbiome were maintained across environments, pair-wise differential abundances of taxa was compared between insectaries. Lines were most similar to other lines from the same insectary than to the same line reared in a different insectary. Additionally, relatively few differentially abundant taxa identified between pairs of lines were shared across insectaries, indicating that line specific properties of the microbiome are not conserved across environments, or that there were distinct microbiota within each insectary. Overall, these results demonstrate that mosquito lines under the same environmental conditions have different microbiomes across microbially- diverse environments and host by microbe interactions affecting microbiome composition and abundance is dependent on environmentally available bacteria.
Copyright: © 2023 Accoti et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Hughes D.A., Bacigalupe R., Wang J., Ruhlemann M.C., Tito R.Y., Falony G., Joossens M., Vieira-Silva S., Henckaerts L., Rymenans L., Verspecht C., Ring S., Franke A., Wade K.H., Timpson N.J., and Raes J., Genome-wide associations of human gut microbiome variation and implications for causal inference analyses. Nat Microbiol, 2020. 5(9): p. 1079–1087 doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0743-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/T001240/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/V011278/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/X018024/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/W018446/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

