CD44-SNA1 integrated cytopathology for delineation of high grade dysplastic and neoplastic oral lesions
- PMID: 37747904
- PMCID: PMC10519609
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291972
CD44-SNA1 integrated cytopathology for delineation of high grade dysplastic and neoplastic oral lesions
Abstract
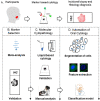
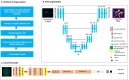
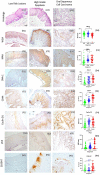
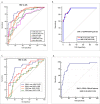
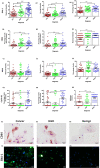
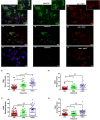
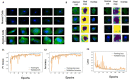
The high prevalence of oral potentially-malignant disorders exhibits diverse severity and risk of malignant transformation, which mandates a Point-of-Care diagnostic tool. Low patient compliance for biopsies underscores the need for minimally-invasive diagnosis. Oral cytology, an apt method, is not clinically applicable due to a lack of definitive diagnostic criteria and subjective interpretation. The primary objective of this study was to identify and evaluate the efficacy of biomarkers for cytology-based delineation of high-risk oral lesions. A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of biomarkers recognized a panel of markers (n: 10) delineating dysplastic oral lesions. In this observational cross sectional study, immunohistochemical validation (n: 131) identified a four-marker panel, CD44, Cyclin D1, SNA-1, and MAA, with the best sensitivity (>75%; AUC>0.75) in delineating benign, hyperplasia, and mild-dysplasia (Low Risk Lesions; LRL) from moderate-severe dysplasia (High Grade Dysplasia: HGD) along with cancer. Independent validation by cytology (n: 133) showed that expression of SNA-1 and CD44 significantly delineate HGD and cancer with high sensitivity (>83%). Multiplex validation in another cohort (n: 138), integrated with a machine learning model incorporating clinical parameters, further improved the sensitivity and specificity (>88%). Additionally, image automation with SNA-1 profiled data set also provided a high sensitivity (sensitivity: 86%). In the present study, cytology with a two-marker panel, detecting aberrant glycosylation and a glycoprotein, provided efficient risk stratification of oral lesions. Our study indicated that use of a two-biomarker panel (CD44/SNA-1) integrated with clinical parameters or SNA-1 with automated image analysis (Sensitivity >85%) or multiplexed two-marker panel analysis (Sensitivity: >90%) provided efficient risk stratification of oral lesions, indicating the significance of biomarker-integrated cytopathology in the development of a Point-of-care assay.
Copyright: © 2023 Sunny et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

