Efficacy of ESHAP versus ICE plus dexamethasone (DICE) as salvage chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 37748107
- PMCID: PMC10521335
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2261109
Efficacy of ESHAP versus ICE plus dexamethasone (DICE) as salvage chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and side effects of salvage chemotherapy between etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine and cisplatin (ESHAP) and ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide plus dexamethasone (DICE) for relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Methods: Medical records of patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL receiving second-line ESHAP or DICE chemotherapy with or without rituximab from January 2007 to November 2022 were retrospectively reviewed. The primary objective was progression-free survival (PFS). The secondary objectives were overall survival (OS), overall response rate (ORR) and adverse events (AEs).
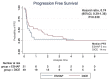
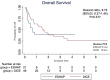
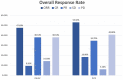
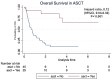
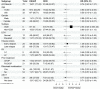
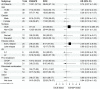
Results: Seventy patients were enrolled including 21 patients who received ESHAP and 49 patients who received the DICE regimen. Six patients (28.6%) and 19 patients (38.8%) in the ESHAP and DICE groups underwent ASCT, respectively. The ORR was 47.6% for ESHAP and 53.1% for DICE (p = .67). The two-year PFS was 14.3% for ESHAP and 26.5% for DICE (p = .33) with median PFS of 5 months and 14 months, respectively (hazard ratio 0.74; 95% CI 0.39-1.36, p = .330). The two-year OS was 14.3% for ESHAP and 26.5% for DICE (p = .37) with median OS of 8 months and 19 months, respectively. Patients in ESHAP group have more all-grade renal impairment than DICE group (23.8% vs. 6.1%, p = .047).
Discussion and conclusions: Efficacy between ESHAP and DICE regimens as salvage chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory DLBCL was not significantly different in terms of two-year PFS, two-year OS and ORR. DICE regimen had less renal AE than ESHAP.
Keywords: DICE chemotherapy; ESHAP chemotherapy; ICE chemotherapy; Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of modified rituximab-ESHAP therapy for relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma.J Chemother. 2010 Feb;22(1):54-7. doi: 10.1179/joc.2010.22.1.54. J Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20227994
-
Lenalidomide in combination with R-ESHAP in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a phase 1b study from GELTAMO group.Br J Haematol. 2016 Apr;173(2):245-52. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13945. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Br J Haematol. 2016. PMID: 26847165 Clinical Trial.
-
R-ESHAP as salvage therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: the influence of prior exposure to rituximab on outcome. A GEL/TAMO study.Haematologica. 2008 Dec;93(12):1829-36. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13440. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Haematologica. 2008. PMID: 18945747
-
Treatment of relapsed aggressive lymphomas: regimens with and without high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002 May;49 Suppl 1:S13-20. doi: 10.1007/s00280-002-0447-1. Epub 2002 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12042984 Review.
-
Quantitative evaluation of therapy options for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A model-based meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Jan;187:106592. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106592. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 36470547 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
