Primaquine dose and the risk of haemolysis in patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis
- PMID: 37748497
- PMCID: PMC7615565
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00431-0
Primaquine dose and the risk of haemolysis in patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Primaquine radical cure is used to treat dormant liver-stage parasites and prevent relapsing Plasmodium vivax malaria but is limited by concerns of haemolysis. We undertook a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis to investigate the haematological safety of different primaquine regimens for P vivax radical cure.
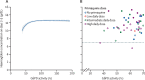
Methods: For this systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis, we searched MEDLINE, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane Central for prospective clinical studies of uncomplicated P vivax from endemic countries published between Jan 1, 2000, and June 8, 2023. We included studies if they had active follow-up of at least 28 days, if they included a treatment group with daily primaquine given over multiple days where primaquine was commenced within 3 days of schizontocidal treatment and was given alone or coadministered with chloroquine or one of four artemisinin-based combination therapies (ie, artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-mefloquine, artesunate-amodiaquine, or dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine), and if they recorded haemoglobin or haematocrit concentrations on day 0. We excluded studies if they were on prevention, prophylaxis, or patients with severe malaria, or if data were extracted retrospectively from medical records outside of a planned trial. For the meta-analysis, we contacted the investigators of eligible trials to request individual patient data and we then pooled data that were made available by Aug 23, 2021. The main outcome was haemoglobin reduction of more than 25% to a concentration of less than 7 g/dL by day 14. Haemoglobin concentration changes between day 0 and days 2-3 and between day 0 and days 5-7 were assessed by mixed-effects linear regression for patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity of (1) 30% or higher and (2) between 30% and less than 70%. The study was registered with PROSPERO, CRD42019154470 and CRD42022303680.
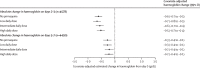
Findings: Of 226 identified studies, 18 studies with patient-level data from 5462 patients from 15 countries were included in the analysis. A haemoglobin reduction of more than 25% to a concentration of less than 7 g/dL occurred in one (0·1%) of 1208 patients treated without primaquine, none of 893 patients treated with a low daily dose of primaquine (<0·375 mg/kg per day), five (0·3%) of 1464 patients treated with an intermediate daily dose (0·375 mg/kg per day to <0·75 mg/kg per day), and six (0·5%) of 1269 patients treated with a high daily dose (≥0·75 mg/kg per day). The covariate-adjusted mean estimated haemoglobin changes at days 2-3 were -0·6 g/dL (95% CI -0·7 to -0·5), -0·7 g/dL (-0·8 to -0·5), -0·6 g/dL (-0·7 to -0·4), and -0·5 g/dL (-0·7 to -0·4), respectively. In 51 patients with G6PD activity between 30% and less than 70%, the adjusted mean haemoglobin concentration on days 2-3 decreased as G6PD activity decreased; two patients in this group who were treated with a high daily dose of primaquine had a reduction of more than 25% to a concentration of less than 7 g/dL. 17 of 18 included studies had a low or unclear risk of bias.
Interpretation: Treatment of patients with G6PD activity of 30% or higher with 0·25-0·5 mg/kg per day primaquine regimens and patients with G6PD activity of 70% or higher with 0·25-1 mg/kg per day regimens were associated with similar risks of haemolysis to those in patients treated without primaquine, supporting the safe use of primaquine radical cure at these doses.
Funding: Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and Medicines for Malaria Venture.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JAG and GCKWK are former employees of GSK and hold shares in GSK and AstraZeneca. GCKWK reports travel support from AstraZeneca. JKB reports institutional research funding from Medicines for Malaria Venture, GSK, Wellcome Trust, and Sanaria; participation on the US National Institutes of Health data safety monitoring board; and membership of the editorial board of Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease and the guidelines development group for malaria control and elimination, Global Malaria Programme, WHO. JKB, RNP, and RJC report contributions to Up-to-Date. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2022. World malaria report 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

