A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes
- PMID: 37748513
- PMCID: PMC10651478
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6
A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes
Abstract
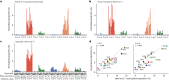
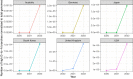
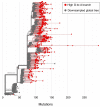
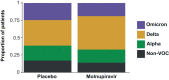
Molnupiravir, an antiviral medication widely used against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), acts by inducing mutations in the virus genome during replication. Most random mutations are likely to be deleterious to the virus and many will be lethal; thus, molnupiravir-induced elevated mutation rates reduce viral load1,2. However, if some patients treated with molnupiravir do not fully clear the SARS-CoV-2 infections, there could be the potential for onward transmission of molnupiravir-mutated viruses. Here we show that SARS-CoV-2 sequencing databases contain extensive evidence of molnupiravir mutagenesis. Using a systematic approach, we find that a specific class of long phylogenetic branches, distinguished by a high proportion of G-to-A and C-to-T mutations, are found almost exclusively in sequences from 2022, after the introduction of molnupiravir treatment, and in countries and age groups with widespread use of the drug. We identify a mutational spectrum, with preferred nucleotide contexts, from viruses in patients known to have been treated with molnupiravir and show that its signature matches that seen in these long branches, in some cases with onward transmission of molnupiravir-derived lineages. Finally, we analyse treatment records to confirm a direct association between these high G-to-A branches and the use of molnupiravir.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




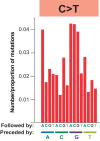
Comment in
-
Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution.Nature. 2023 Nov;623(7987):486-487. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37875683 No abstract available.
References
-
- NICE Recommends 3 Treatments for COVID-19 in Draft Guidance. National Institute for Health and Care Excellencehttps://www.nice.org.uk/news/article/nice-recommends-3-treatments-for-co... (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

