Characterization and structure-based protein engineering of a regiospecific saponin acetyltransferase from Astragalus membranaceus
- PMID: 37749089
- PMCID: PMC10519980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41599-7
Characterization and structure-based protein engineering of a regiospecific saponin acetyltransferase from Astragalus membranaceus
Abstract
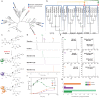
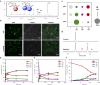
Acetylation contributes to the bioactivity of numerous medicinally important natural products. However, little is known about the acetylation on sugar moieties. Here we report a saponin acetyltransferase from Astragalus membranaceus. AmAT7-3 is discovered through a stepwise gene mining approach and characterized as the xylose C3'/C4'-O-acetyltransferse of astragaloside IV (1). To elucidate its catalytic mechanism, complex crystal structures of AmAT7-3/1 and AmAT7-3A310G/1 are obtained, which reveal a large active pocket decided by a specific sequence AADAG. Combining with QM/MM computation, the regiospecificity of AmAT7-3 is determined by sugar positioning modulated by surrounding amino acids including #A310 and #L290. Furthermore, a small mutant library is built using semi-rational design, where variants A310G and A310W are found to catalyze specific C3'-O and C4'-O acetylation, respectively. AmAT7-3 and its variants are also employed to acetylate other bioactive saponins. This work expands the understanding of saponin acetyltransferases, and provide efficient catalytic tools for saponin acetylation.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Osbourn A, Goss RJ, Field RA. The saponins: polar isoprenoids with important and diverse biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011;28:1261–1268. - PubMed
-
- Challinor VL, De Voss JJ. Open-chain steroidal glycosides, a diverse class of plant saponins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013;30:429–454. - PubMed
-
- Moreau RA, Whitaker BD, Hicks KB. Phytosterols, phytostanols, and their conjugates in foods: structural diversity, quantitative analysis, and health-promoting uses. Prog. Lipid Res. 2002;41:457–500. - PubMed
-
- Reed J, et al. Elucidation of the pathway for biosynthesis of saponin adjuvants from the soapbark tree. Science. 2023;379:1252–1264. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Lee Y, Park J, Lee S. Ginsenoside-Rs4, a new type of ginseng saponin concurrently induces apoptosis and selectively elevates protein levels of p53 and p21WAF1 in human hepatoma SK-HEP-1 cells. Eur. J. Cancer. 1999;35:507–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

