Successful remission induction of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by obinutuzumab therapy: a retrospective study of 8 patients
- PMID: 37749377
- PMCID: PMC10920806
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-023-02758-8
Successful remission induction of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by obinutuzumab therapy: a retrospective study of 8 patients
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the therapeutic efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in remission induction for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) patients.
Methods: Eight IgG4-ROD patients were retrospectively enrolled. They were intravenously administered 1000 mg obinutuzumab at baseline and examined for changes in physical signs, orbital structure imaging parameters, IgG4-related disease responder index (IgG4-RD RI), serological index, and adverse events during treatment. The number of treatment sessions was based on treatment response.
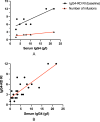
Results: The mean IgG4-RD RI scores of all patients at baseline (7.75 ± 2.92) and after treatment (2.00 ± 0.76) were highly significantly different (P < 0.001). Six patients achieved complete remission (CR) (75%) and two patients achieved partial remission (25%). The mean serum IgG4 levels at baseline (9.45 ± 6.95 g/L) and after treatment (1.55 ± 1.09 g/L) showed a mean decrease of 83% (P = 0.0079). The serum IgG4 level correlated well with IgG4-RD RI at baseline and that after each treatment (r = 0.852, P < 0.01; r = 0.78, P < 0.001). In patients with CR, the serum IgG4 levels at baseline correlated positively with dose numbers required for CR (r = 0.86, P < 0.05). Five patients (62.5%) experienced infusion-related reactions (IRRs) during the first obinutuzumab infusion, while only one (12.5%) experienced IRRs during all subsequent eight infusions.
Conclusion: Obinutuzumab is a safe and promising therapeutic option for IgG4-ROD. It rapidly reduces ocular inflammation and serum IgG4 levels to avoid excessive corticosteroid usage and reduce potential risk of adverse events.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Royal College of Ophthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of iguratimod on patients with relapsed or refractory IgG4-related disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;39(2):491-497. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04880-z. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31848912
-
Combination therapy of leflunomide and glucocorticoids for the maintenance of remission in patients with IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study and literature review.Intern Med J. 2017 Jun;47(6):680-689. doi: 10.1111/imj.13430. Intern Med J. 2017. PMID: 28321964 Review.
-
Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jun;74(6):1171-7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206605. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25667206
-
Efficacy between high and medium doses of glucocorticoid therapy in remission induction of IgG4-related diseases: a preliminary randomized controlled trial.Int J Rheum Dis. 2017 May;20(5):639-646. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13088. Epub 2017 May 29. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28556584 Clinical Trial.
-
IgG4-related disease administered dupilumab: case series and review of the literature.RMD Open. 2023 Mar;9(1):e003026. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003026. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 36894196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Management of IgG4-Related Disease: From Traditional to Mechanism-Based Targeted Therapies.Drugs Aging. 2025 Feb;42(2):111-126. doi: 10.1007/s40266-024-01172-3. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Drugs Aging. 2025. PMID: 39755996 Review.
-
[The combined regimen based on obinutuzumab plus glucocorticoid for 4 cases of relapsed iTTP].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jan 14;46(1):70-74. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121090-20241107-00437. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40059685 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

