Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of cholesterol based on Au-Pt NPs/PAMAM-ZIF-67 nanomaterials
- PMID: 37749481
- PMCID: PMC10766835
- DOI: 10.1007/s44211-023-00427-0
Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of cholesterol based on Au-Pt NPs/PAMAM-ZIF-67 nanomaterials
Abstract
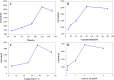
A cholesterol biosensor was constructed by bimetallic (Au and Pt) and poly(amidoamine)-zeolite imidazole framework (PAMAM-ZIF-67). First, PAMAM-ZIF-67 nanomaterial was immobilized onto the electrode, and then Au and Pt were modified on the electrode by the electro-deposition method. Subsequently, cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) and cholesterol esterase (ChEt) were fixed on the electrode. The stepwise modification procedures were recorded by impedance spectroscopy and voltammetry. The current response presented a linear relation to the logarithm of cholesterol content when content ranged between 0.00015 and 10.24 mM, and the minimum detection concentration reached 3 nM. The electrode was also used for the cholesterol assay in serum, which hinted at its potentially valuable in clinical diagnostics. An electrochemical biosensor based on gold nanoparticles, platinum nanoparticles, and polyamide-zeolitic imidazolate frameworks was developed for detection of cholesterol. First, polyamide-zeolitic imidazolate frameworks nanomaterial was fixed onto the electrode modified of mercaptopropionic acid by Au-S bond. Then, gold nanoparticles and platinum nanoparticles were electrodeposited on the above electrode. Subsequently, cholesterol oxidase and cholesterol esterase were co-immobilized on the surface of the modified electrode to fabricate the cholesterol biosensor. The biosensor has also been used for the measurement of cholesterol in human serum, which implied potential applications in biotechnology and clinical diagnostics.
Keywords: Biosensor; Cholesterol; Nanoparticles; Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

