Prevalence and associated factors of non-medical use of prescription drugs among adolescents in secondary schools in Buea, Cameroon: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37749516
- PMCID: PMC10521405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-023-05120-0
Prevalence and associated factors of non-medical use of prescription drugs among adolescents in secondary schools in Buea, Cameroon: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The non-medical use of prescription drugs is a growing public health problem worldwide. Recent trends in Cameroon show that the use of psychoactive substances, among which are prescription drugs by adolescents is becoming a public health issue and is linked to juvenile delinquency and violence in schools. However, there is a paucity of data on the burden of this phenomenon among adolescent secondary school students in the country. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and factors associated with the use of non-prescription drugs in secondary schools in Buea, South West region of Cameroon.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study from 1st February 2021 to 30th April 2021. Secondary school students were recruited using a multistage stratified cluster sampling. A modified and standardized version of the World Health Organization student drug-use survey model questionnaire was used. Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Buea (No. 2021/1273-02/UB/SG/IRB/FHS). The Statistical Package for Social Sciences, IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. was used for data analysis. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the sociodemographic characteristics of participants. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were used to explore associated factors of non-medical use of prescription drugs.
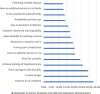
Results: A total of 570 participants were enrolled for the study, and 510 participants responded giving a response rate of 89.5%. The prevalence of non-medical use of prescription drugs was 15.3%, tramadol being the most used. Motivators for non-medical use of prescription drugs were "to work longer", "to be courageous", and "curiosity". Logistic regression results showed that alcohol consumption [OR 3.68; 95% CI: 2.24-6.06; p < 0.001], smoking [OR 6.00; 95% CI: 3.07-11.75; p < 0.001] and use of illicit drugs [OR 10.85; 95% CI: 5.48-21.48; p < 0.001] were independent factors associated with non-medical use of prescription drugs.
Conclusion: Non-medical use of prescription drugs was prevalent among adolescent secondary school students in Buea, Cameroon. Tramadol is the main drug of prescription involved. Our results can guide policymakers on strategies to screen, prevent and control non-medical use of prescription drugs among secondary school students in Cameroon.
Keywords: Adolescent; Non-medical use; Prescription drugs; Secondary school students; Tramadol.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substance use among students of two high schools in Yaoundé, Cameroon.Pan Afr Med J. 2024 Dec 16;49:121. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.49.121.43487. eCollection 2024. Pan Afr Med J. 2024. PMID: 40190426 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with substance use among students in tertiary institutions in Buea, Cameroon.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 Feb 4;41:103. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.41.103.29272. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 35432698 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predictors of recreational drug use among medical and nursing students in Cameroon: a cross sectional analysis.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Jul 28;11(1):515. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3631-z. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 30055652 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and risk factors associated with hypertension among adults in a rural setting: the case of Ombe, Cameroon.Pan Afr Med J. 2019 Nov 14;34:147. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2019.34.147.17518. eCollection 2019. Pan Afr Med J. 2019. PMID: 32117515 Free PMC article.
-
Sociodemographic profile of psychoactive substance use among selected secondary school students in rural Nigeria.Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2020 Sep 2;34(5):275-280. doi: 10.1515/ijamh-2020-0086. eCollection 2022 Oct 1. Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2020. PMID: 32887185
Cited by
-
Substance use among students of two high schools in Yaoundé, Cameroon.Pan Afr Med J. 2024 Dec 16;49:121. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.49.121.43487. eCollection 2024. Pan Afr Med J. 2024. PMID: 40190426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). The non-medical use of prescription drugs: Policy direction issues. 2011.
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). World Drug Report. 2022. UNODC, World Drug Report 2022 (United Nations publication, 2022). Available from: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/world-drug-report-2022..... Cited 2023 Jan 19.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous