Raptor mediates the selective inhibitory effect of cardamonin on RRAGC-mutant B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 37749558
- PMCID: PMC10521446
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04166-7
Raptor mediates the selective inhibitory effect of cardamonin on RRAGC-mutant B cell lymphoma
Abstract
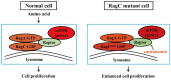
Background: mTORC1 (mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1) is associated with lymphoma progression. Oncogenic RRAGC (Rag guanosine triphosphatase C) mutations identified in patients with follicular lymphoma facilitate the interaction between Raptor (regulatory protein associated with mTOR) and Rag GTPase. It promotes the activation of mTORC1 and accelerates lymphomagenesis. Cardamonin inhibits mTORC1 by decreasing the protein level of Raptor. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effect and possible mechanism of action of cardamonin in RRAGC-mutant lymphoma. This could provide a precise targeted therapy for lymphoma with RRAGC mutations.
Methods: Cell viability was measured using a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Protein expression and phosphorylation levels were determined using western blotting. The interactions of mTOR and Raptor with RagC were determined by co-immunoprecipitation. Cells overexpressing RagC wild-type (RagCWT) and RagC Thr90Asn (RagCT90N) were generated by lentiviral infection. Raptor knockdown was performed by lentivirus-mediated shRNA transduction. The in vivo anti-tumour effect of cardamonin was assessed in a xenograft model.
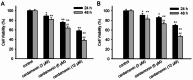
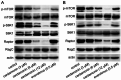
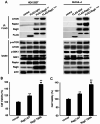
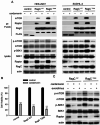
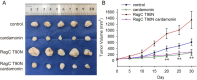
Results: Cardamonin disrupted mTOR complex interactions by decreasing Raptor protein levels. RagCT90N overexpression via lentiviral infection increased cell proliferation and mTORC1 activation. The viability and tumour growth rate of RagCT90N-mutant cells were more sensitive to cardamonin treatment than those of normal and RagCWT cells. Cardamonin also exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect on the phosphorylation of mTOR and p70 S6 kinase 1 in RagCT90N-mutant cells. Raptor knockdown abolishes the inhibitory effects of cardamonin on mTOR. An in vivo xenograft model demonstrated that the RagCT90N-mutant showed significantly higher sensitivity to cardamonin treatment.
Conclusions: Cardamonin exerts selective therapeutic effects on RagCT90N-mutant cells. Cardamonin can serve as a drug for individualised therapy for follicular lymphoma with RRAGC mutations.
Keywords: Cardamonin; Follicular lymphoma; RagC; Raptor; mTORC1.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autophagy induced by cardamonin is associated with mTORC1 inhibition in SKOV3 cells.Pharmacol Rep. 2018 Oct;70(5):908-916. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Pharmacol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30099297
-
Recurrent Mutations in the MTOR Regulator RRAGC in Follicular Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;22(21):5383-5393. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0609. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27267853 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acids activate mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 without changing Rag GTPase guanyl nucleotide charging.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 31;289(5):2658-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.528505. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24337580 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid regulation of TOR complex 1.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Apr;296(4):E592-602. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90645.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 18765678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New structures of mTORC1: Focus on Rag GTPases].Med Sci (Paris). 2021 Apr;37(4):372-378. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2021033. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Med Sci (Paris). 2021. PMID: 33908855 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Cardamonin suppresses mTORC1/SREBP1 through reducing Raptor and inhibits de novo lipogenesis in ovarian cancer.PLoS One. 2025 May 2;20(5):e0322733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322733. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40315213 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

