Automatic evaluation of atlantoaxial subluxation in rheumatoid arthritis by a deep learning model
- PMID: 37749583
- PMCID: PMC10518918
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-023-03172-x
Automatic evaluation of atlantoaxial subluxation in rheumatoid arthritis by a deep learning model
Abstract
Background: This work aims to develop a deep learning model, assessing atlantoaxial subluxation (AAS) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which can often be ambiguous in clinical practice.
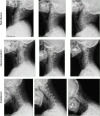
Methods: We collected 4691 X-ray images of the cervical spine of the 906 patients with RA. Among these images, 3480 were used for training the deep learning model, 803 were used for validating the model during the training process, and the remaining 408 were used for testing the performance of the trained model. The two-dimensional key points' detection model of Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation was adopted as the base convolutional neural network model. The model inferred four coordinates to calculate the atlantodental interval (ADI) and space available for the spinal cord (SAC). Finally, these values were compared with those by clinicians to evaluate the performance of the model.
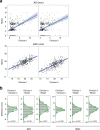
Results: Among the 408 cervical images for testing the performance, the trained model correctly identified the four coordinates in 99.5% of the dataset. The values of ADI and SAC were positively correlated among the model and two clinicians. The sensitivity of AAS diagnosis with ADI or SAC by the model was 0.86 and 0.97 respectively. The specificity of that was 0.57 and 0.5 respectively.
Conclusions: We present the development of a deep learning model for the evaluation of cervical lesions of patients with RA. The model was demonstrably shown to be useful for quantitative evaluation.
Keywords: Atlantoaxial subluxation; Cervical spine; Deep learning; Machine learning; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiological evaluation of cervical spine involvement in rheumatoid arthritis.Neurosurg Focus. 2015 Apr;38(4):E4. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.FOCUS14664. Neurosurg Focus. 2015. PMID: 25828498 Review.
-
Influence of systemic bone mineral density on atlantoaxial subluxation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Osteoporos Int. 2017 Jun;28(6):1931-1938. doi: 10.1007/s00198-017-3972-9. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Osteoporos Int. 2017. PMID: 28255666
-
Incidence and aggravation of cervical spine instabilities in rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective minimum 5-year follow-up study of patients initially without cervical involvement.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Dec 15;37(26):2136-44. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31826def1c. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22895480
-
Subaxial subluxation after atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation in rheumatoid patients.Eur Spine J. 2009 Jun;18(6):869-76. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-0945-5. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Eur Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19337758 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological assessment and surgical management of cervical spine involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2023 Feb;43(2):195-208. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05239-5. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 36378323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning analysis for rheumatologic imaging: current trends, future directions, and the role of human.J Rheum Dis. 2025 Apr 1;32(2):73-88. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0128. Epub 2025 Jan 20. J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 40134548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current application, possibilities, and challenges of artificial intelligence in the management of rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2025 Jun 21;17:1759720X251343579. doi: 10.1177/1759720X251343579. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2025. PMID: 40547599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research on a deep learning-based model for measurement of X-ray imaging parameters of atlantoaxial joint.Eur Spine J. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.1007/s00586-025-09075-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Spine J. 2025. PMID: 40637839
-
A machine learning based quantification system for automated diagnosis of lumbar spondylolisthesis on spinal X-rays.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 4;10(17):e37418. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37418. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39290282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cabot A, Becker A. The cervical spine in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;131:130–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

