Neoadjuvant sintilimab combined with chemotherapy in resectable locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: case series and literature review
- PMID: 37749594
- PMCID: PMC10521519
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-023-03194-4
Neoadjuvant sintilimab combined with chemotherapy in resectable locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: case series and literature review
Abstract
Background: In recent years, neoadjuvant immunotherapy with chemotherapy has shown increasing promise for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, to establish its clinical efficacy and safety, it is imperative to amass more real-world clinical data. This retrospective study aims to assess the safety and effectiveness of combing sintilimab, a PD-1 inhibitor, with chemotherapy as a neoadjuvant treatment modality in patients diagnosed with potentially resectable NSCLC.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed patients with stage II-III NSCLC receiving neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy in Sichuan Cancer Hospital between February 2021 and February 2023. Sintilimab injection (intravenously,200 mg, iv, d1, q3w) and platinum-based chemotherapy were administered intravenously every 3 weeks, with radical lung cancer resection planned approximately 4-11 weeks after the last dose. The primary endpoint of the study was pathologic complete response (pCR). The secondary endpoints were objective response rate (ORR), and safety.
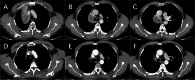
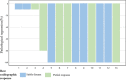
Result: Thirteen patients were enrolled, they were mostly diagnosed with stage III NSCLC (IIB 15.4% IIIA 38.5%; IIIB 46.2%). Most of them had pathologically confirmed squamous cell carcinoma (69.2%). All patients received sintilimab combined with platinum-based chemotherapy for 2 to 4 cycles. Notably, none of the patients necessitated a reduction in initial dosages or treatment postponement due to intolerable adverse events. Then, all of them underwent surgical operation. Impressively, nine patients (69.2%) achieved a pathologic complete response. The objective response rate (ORR) stood at 46.15%. Nine patients experienced neoadjuvant treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), with only one patient (7.6%) encountering a grade 4 neoadjuvant TRAE.
Conclusion: Therefore, the current study suggested that neoadjuvant sintilimab plus platinum-based chemotherapy can be a safe approach in increasing the efficiency of treatment and hopefully improving the prognosis of patients with potentially resectable locally advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: Chemoimmunotherapy; Neoadjuvant; Non-small cell lung carcinoma; PD-1(programmed cell death protein 1); Sintilimab.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interim analysis of the efficiency and safety of neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor (sintilimab) combined with chemotherapy (nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin) in potentially resectable stage IIIA/IIIB non-small cell lung cancer: a single-arm, phase 2 trial.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Feb;149(2):819-831. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03896-w. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35192053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of perioperative sintilimab plus platinum-based chemotherapy for potentially resectable stage IIIB non-small cell lung cancer (periSCOPE): an open-label, single-arm, phase II trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Dec 7;79:102997. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102997. eCollection 2025 Jan. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39720604 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency and safety of neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor (sintilimab) combined with chemotherapy in potentially resectable stage IIIA/IIIB non-small cell lung cancer: Neo-Pre-IC, a single-arm phase 2 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Jan 19;68:102422. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102422. eCollection 2024 Feb. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38304743 Free PMC article.
-
NeoSCORE II: three vs four cycles of neoadjuvant sintilimab + chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2024 Jan;20(3):121-129. doi: 10.2217/fon-2024-0026. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38353107 Review.
-
Pathological complete response to neoadjuvant tislelizumab plus chemotherapy in stage IIIB small cell lung cancer: A case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1111325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1111325. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sintilimab for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma-induced immune-related hypophysitis: a case report.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;16:1534179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1534179. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39917296 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression of ANAPC1 in lung squamous cell carcinoma: clinical implications and mechanisms.Future Sci OA. 2025 Dec;11(1):2482487. doi: 10.1080/20565623.2025.2482487. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Future Sci OA. 2025. PMID: 40139913 Free PMC article.
-
Role of immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy in recurrent drug-resistant gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: Four case reports and literature review.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Mar;7(3):e2016. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2016. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38425251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant immunotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of phase 3 clinical trials.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1359302. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1359302. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646542 Free PMC article.
-
Novel FABP4+C1q+ macrophages enhance antitumor immunity and associated with response to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab and chemotherapy in NSCLC via AMPK/JAK/STAT axis.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(10):717. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07074-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39353883 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pless M, Stupp R, Ris HB, Stahel RA, Weder W, Thierstein S, Gerard MA, Xyrafas A, Früh M, Cathomas R, Zippelius A, Roth A, Bijelovic M, Ochsenbein A, Meier UR, Mamot C, Rauch D, Gautschi O, Betticher DC, Mirimanoff RO, Peters S; SAKK Lung Cancer Project Group. Induction chemoradiation in stage IIIA/N2 non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet. 2015;386(9998):1049–56. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Blake SJ, Yong MCR, Harjunpää H, Ngiow SF, Takeda K, Young A, O'Donnell JS, Allen S, Smyth MJ, Teng MWL. Improved efficacy of neoadjuvant compared to adjuvant immunotherapy to eradicate metastatic disease. Cancer Discov. 2016;6(12):1382–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials